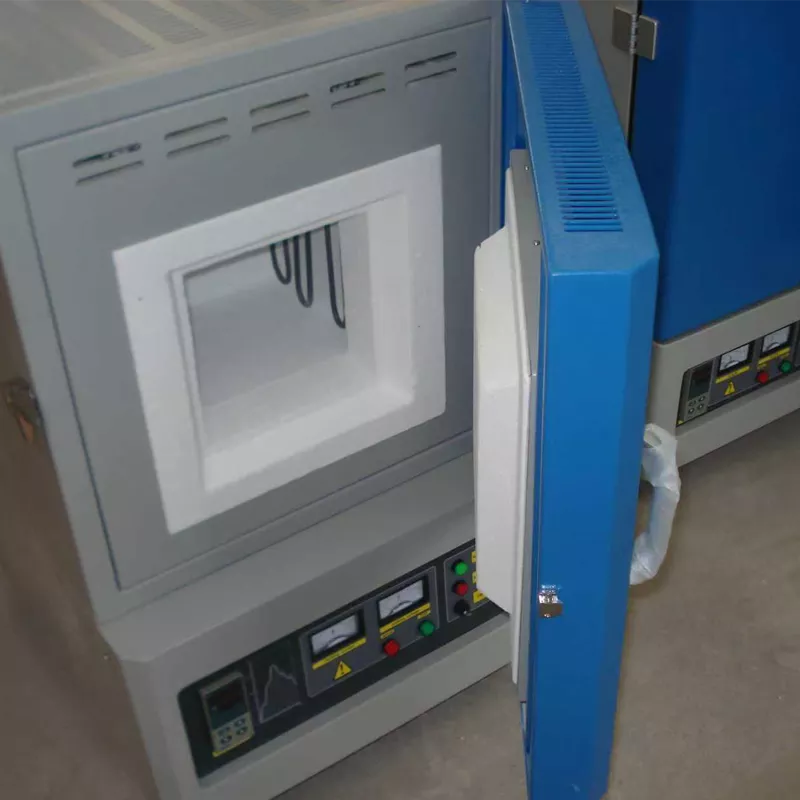
Signes d'un chauffage inégal et d'une montée en température lente
En laboratoire ou en milieu industriel, four à moufle sont souvent confrontés à ces problèmes révélateurs :
- La température réglée n'atteint pas la valeur cible.
- Des gradients de température significatifs apparaissent dans les zones du four (par exemple, des variations de haut en bas ou d'avant en arrière).
- Les taux de chauffage ralentissent sensiblement par rapport à une unité neuve.
- Les échantillons présentent un frittage irrégulier ou les résultats d'analyse sont entachés d'erreurs accrues.
Ces symptômes indiquent généralement une perturbation du champ thermique interne ou une dérive du système de contrôle.
Aujourd'hui, CVSIC actions prouvées causes et remèdes pour un chauffage irrégulier de la chaudière à moufle, vous permettant de diagnostiquer et de résoudre rapidement les problèmes afin d'obtenir des performances fiables.

Causes courantes et solutions pour un chauffage inégal dans les chaudières à moufle
Un chauffage inégal se produit lorsque la distribution de la température dans la chambre du four varie de manière significative, souvent sous la forme d'un centre chaud avec des bords plus froids ou des points chauds isolés. Cela peut compromettre l'intégrité de l'échantillon, par exemple en entraînant un frittage irrégulier de la céramique. Nous décrivons ci-dessous les principales causes et les remèdes pratiques.
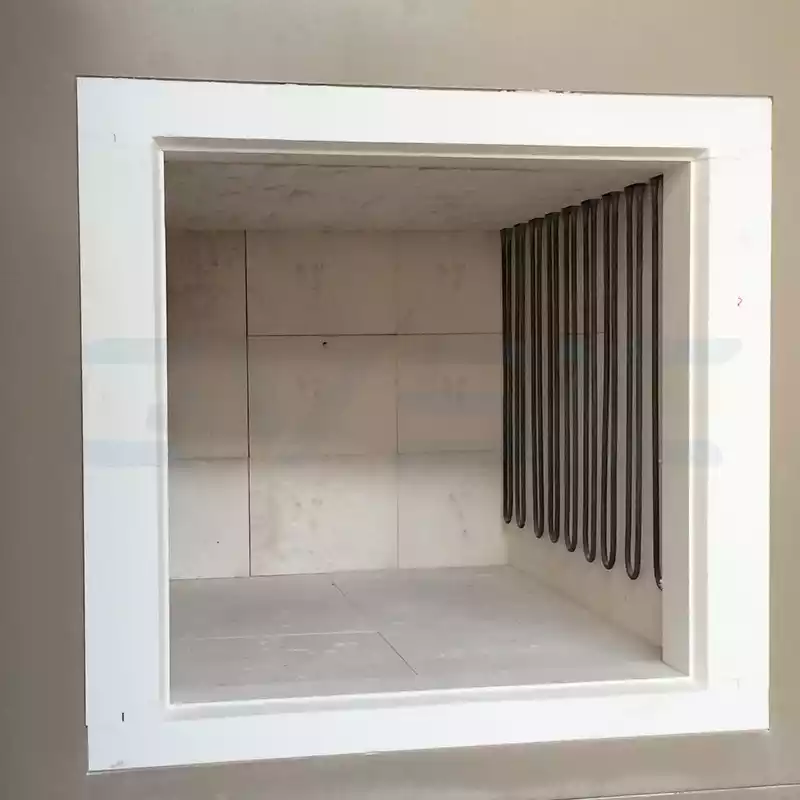
Répartition inégale ou vieillissement des éléments chauffants
- Fours à fil de résistance(<1200℃) : L'exposition prolongée à des températures élevées provoque une oxydation qui augmente la résistance et réduit le rendement thermique.
- Éléments SiC (1400℃) : Au cours de cycles prolongés, la résistance augmente rapidement, ce qui se traduit par des températures plus basses dans les éléments concernés.
- Éléments MoSi2 (1600-1800℃) : Les ruptures fragiles ou l'oxydation de l'embout perturbent l'échauffement localisé.
- Dans l'ensemble, une mauvaise installation ou un vieillissement localisé entraîne un rayonnement thermique incohérent.
Solutions:
- Utilisez un multimètre pour vérifier la cohérence de la résistance entre les zones de chauffage.
- Remplacer un élément si la résistance dépasse la valeur initiale de plus de 20%.
- Effectuer un nettoyage mensuel pour éliminer la poussière de surface et l'accumulation d'oxyde.
- Limiter les vitesses de rampe à moins de 10°C/min pour éviter les contraintes thermiques et prolonger la durée de vie des éléments.
Comment déterminer si les éléments chauffants d'un four à moufle doivent être remplacés ?
Vieillissement ou endommagement de l'isolation de la chambre du four
- Briques d'isolation ou panneaux de fibres céramiques peuvent se pulvériser ou se fissurer après une exposition prolongée à la chaleur, ce qui permet à la chaleur de s'échapper.
- Des joints de porte de four mal fixés créent des interstices qui favorisent les “points froids” en laissant échapper de la chaleur.
Solutions:
- Inspecter les parois de la chambre et les joints d'étanchéité des portes pour vérifier qu'il n'y a pas de fissures, et les remplacer rapidement si nécessaire.
- Utiliser une caméra thermique pour localiser les fuites.
- Pour un fonctionnement durable, remplacer la couche d'isolation tous les 2 ou 3 ans pour maintenir l'efficacité.
Vieillissement ou désalignement des thermocouples (capteurs de température)
- L'oxydation ou un mauvais positionnement empêche le régulateur PID de détecter avec précision les températures réelles, ce qui déclenche une surcompensation ou une sous-compensation.
- Cela se traduit souvent par des affichages réguliers alors que la température réelle du four est basse.
Solutions:
- Confirmer que la profondeur d'insertion du thermocouple est conforme aux directives du fabricant (généralement un tiers au milieu de la chambre).
- Calibrer avec un thermomètre standard pour plus de précision.
- Remplacer ou recalibrer toutes les 1 000 heures de fonctionnement pour assurer un contrôle précis.
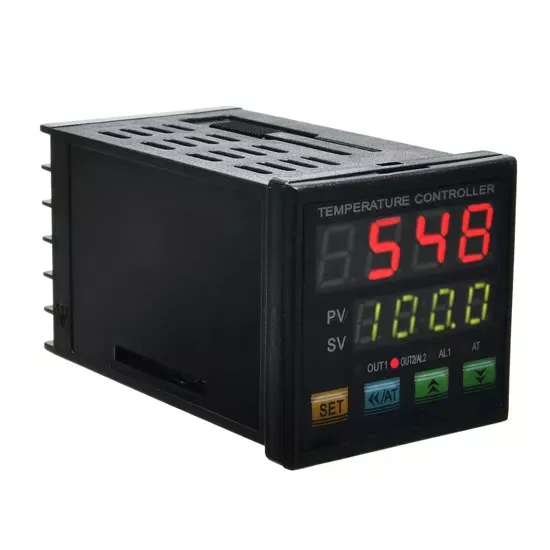
Paramètres de contrôle PID inappropriés ou défaillances du module
- Sous-optimale PID (valeurs P, I, D) peut entraîner des cycles de dépassement et de sous-réglage ou des réponses de chauffage retardées.
- Des modules de contrôle de la température dégradés ou des relais de courant défectueux nuisent encore plus à la stabilité du chauffage.
Solutions:
- Exécuter un processus d'autoréglage pour réinitialiser les paramètres PID.
- Inspecter les relais de la carte de contrôle et les connexions d'alimentation pour s'assurer qu'ils ne sont pas desserrés.
- Pour les fours à moufle industriels, envisagez de passer à un système de contrôle PLC modulaire pour une plus grande fiabilité.
Tension d'alimentation insuffisante ou mauvais contacts électriques
- La tension d'alimentation chute en dessous des niveaux nominaux (par exemple, de 380V à 360V), ce qui entraîne une coupure directe de l'alimentation.
- Les lignes électriques vieillies, oxydées ou détachées introduisent des fluctuations de courant.
Solutions:
- Mesurer la tension d'entrée et confirmer qu'elle se situe à ±5% de la valeur nominale.
- Serrer les vis des bornes sur les connexions d'alimentation pour sécuriser les contacts.
- Installez un stabilisateur de tension ou un protecteur de circuit dédié si les fluctuations persistent.
Chargement incorrect de l'échantillon ou flux d'air restreint
- Les échantillons surchargés ou les plateaux qui bloquent la circulation créent une dispersion inégale de la chaleur.
- Une convection limitée retarde le réchauffement local, ralentissant la montée en puissance globale.
Solutions:
- Maintenir un espace d'au moins 2-3 cm entre les échantillons et les parois du four pour assurer un flux d'air régulier.
- Optez pour des plateaux résistants aux températures élevées au lieu de placer les objets directement sur le sol.
- Pour le chauffage de grands volumes, il convient d'opter pour des fours à zones multiples afin d'optimiser l'uniformité.
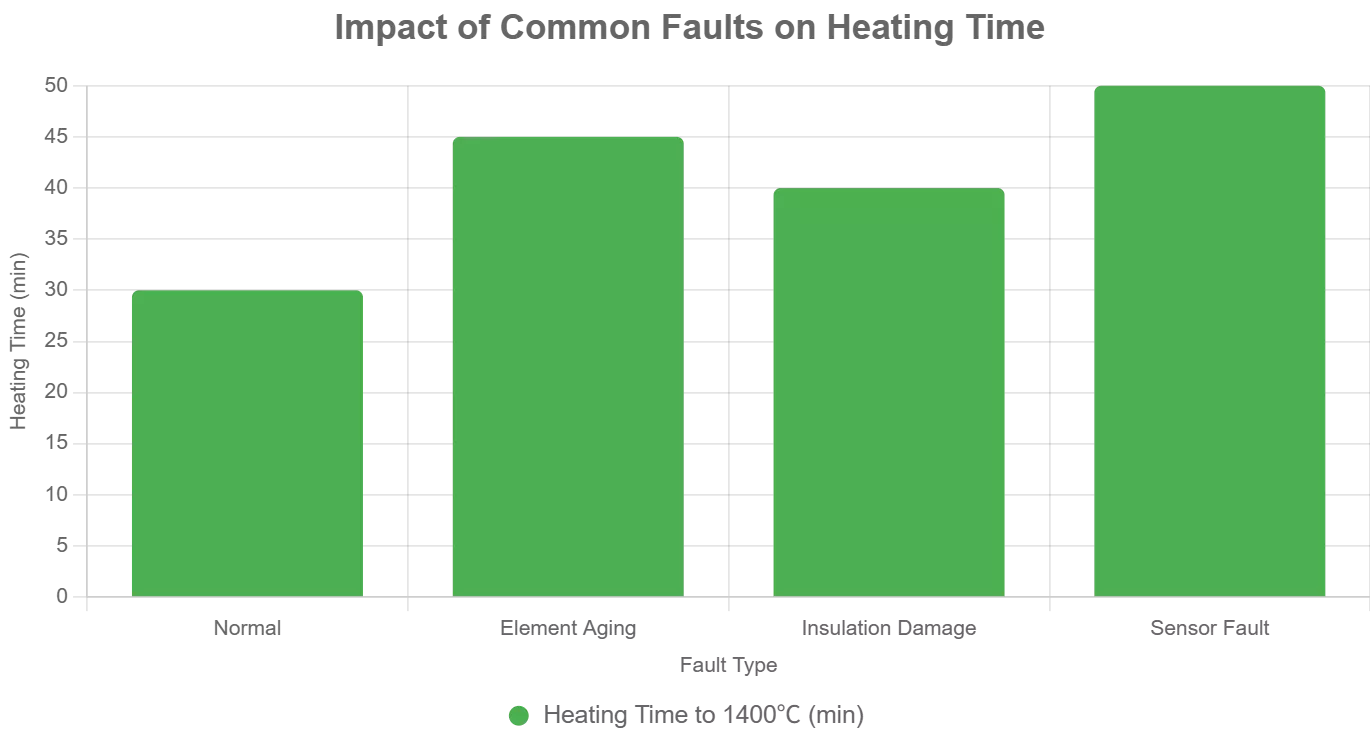
Impact des défauts courants sur le temps de chauffe
Le diagramme ci-dessous illustre comment les défauts typiques affectent les temps de montée en puissance (d'après les données du CVSIC) :
Diagnostic complet et recommandations d'entretien
| Problème observé | Causes possibles | Méthodes de diagnostic rapide |
| Chauffage lent | Résistance accrue, tension insuffisante | Mesurer les variations de courant et de résistance |
| Température inégale | Vieillissement des composants, détérioration de l'isolation | Imagerie thermique du champ de chaleur |
| Fluctuations de température | Dysfonctionnement du thermocouple ou du PID | Comparer les températures réelles et les températures affichées |
| Surchauffe localisée | Obstruction de l'échantillon, mauvaise circulation de l'air | Ajuster les chemins de chargement et de ventilation |
Recommandations des ingénieurs du CVSIC
- Inspectez les fours de laboratoire très utilisés tous les trois mois pour qu'ils fonctionnent au mieux.
- N'utilisez que des éléments chauffants et des thermocouples certifiés par l'équipementier pour éviter les problèmes et augmenter la durée de vie de l'équipement.
- Si le taux de chauffage chute de 15% ou plus, vérifiez immédiatement la puissance de sortie afin d'éviter les temps d'arrêt.
Conclusion
L'efficacité de la chaudière Muffle dépend entretien, et pas seulement la conception.
Engagez-vous dans un programme d'entretien régulier avec CVSIC ou consultez notre équipe d'ingénieurs pour des plans d'entretien personnalisés. Cela permet de garantir des performances fiables et de respecter les normes d'ingénierie de CVSIC pour une expérience utilisateur sans faille.
Vous pouvez avoir besoin de savoir :