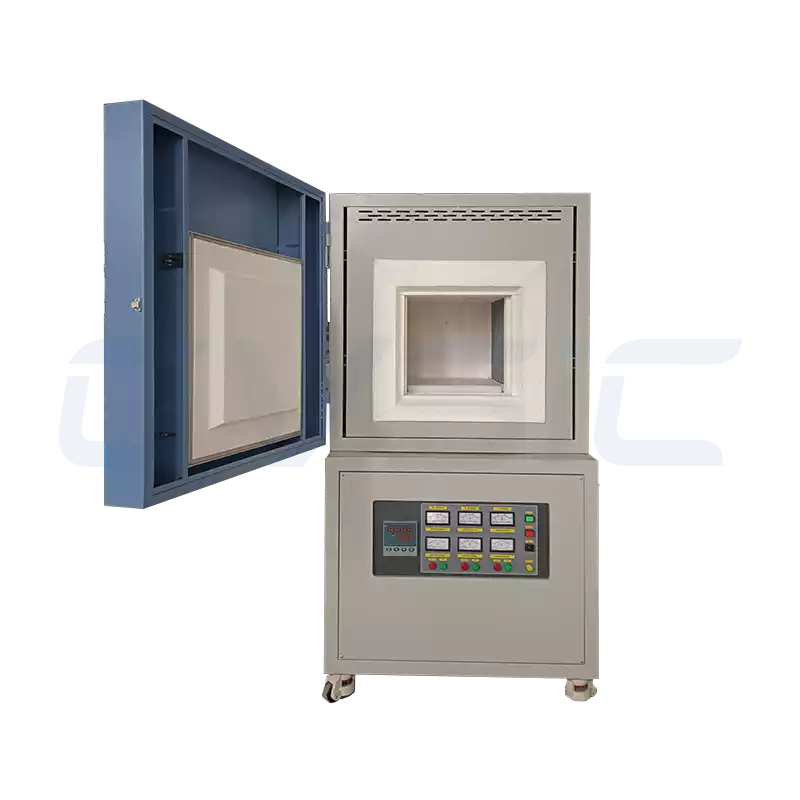
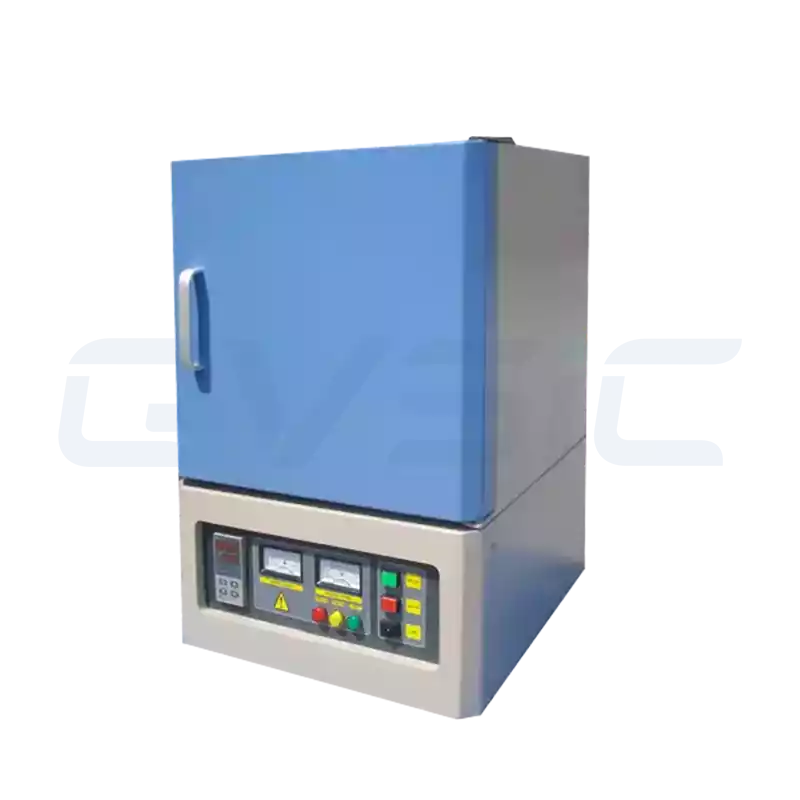
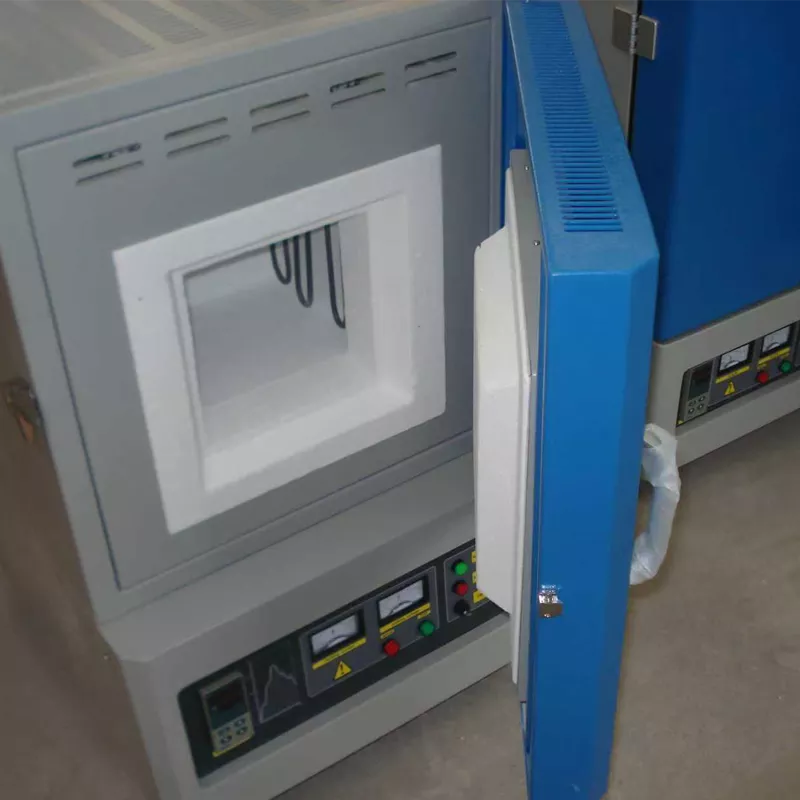
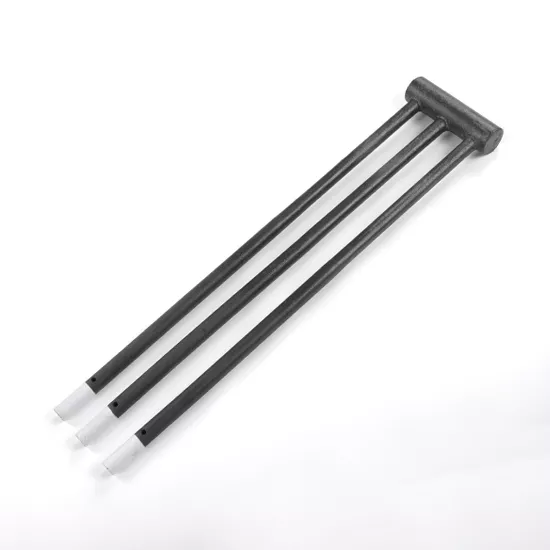
In materials research and high-temperature testing, a 1800°C muffle furnace embodies peak heating performance.
Beyond 1700°C, many standard materials reach or exceed their softening points. This requires superior thermal stability and oxidation resistance in the furnace shell, insulation, and heating parts.
Engineered specifically for these extreme high-temperature applications, the 1800°C muffle furnace goes beyond mere elevated temperatures—it’s an essential gateway to advanced ceramics, functional materials, and innovative composites. To understand its practical capabilities, consider the specialized processes and materials it enables.
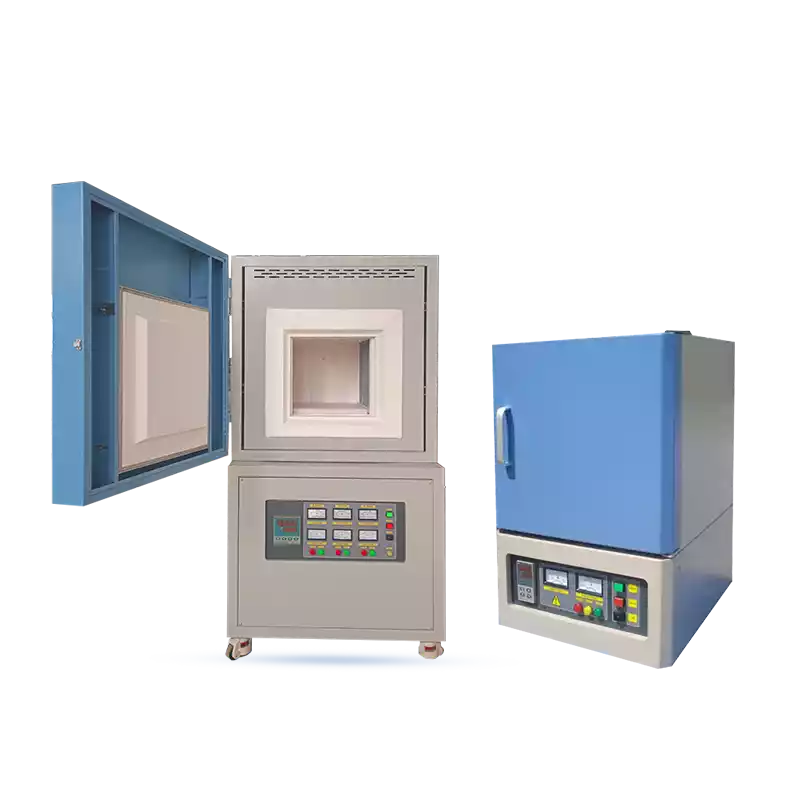

What Does 1800°C Enable?
This peak temperature allows reliable execution of demanding tasks, including:
- High-temperature ceramic sintering
- Refractory metal sintering and annealing
- Glass and crystal melting
- Powder metallurgy densification
- Phase transformation and microstructural control in novel materials.
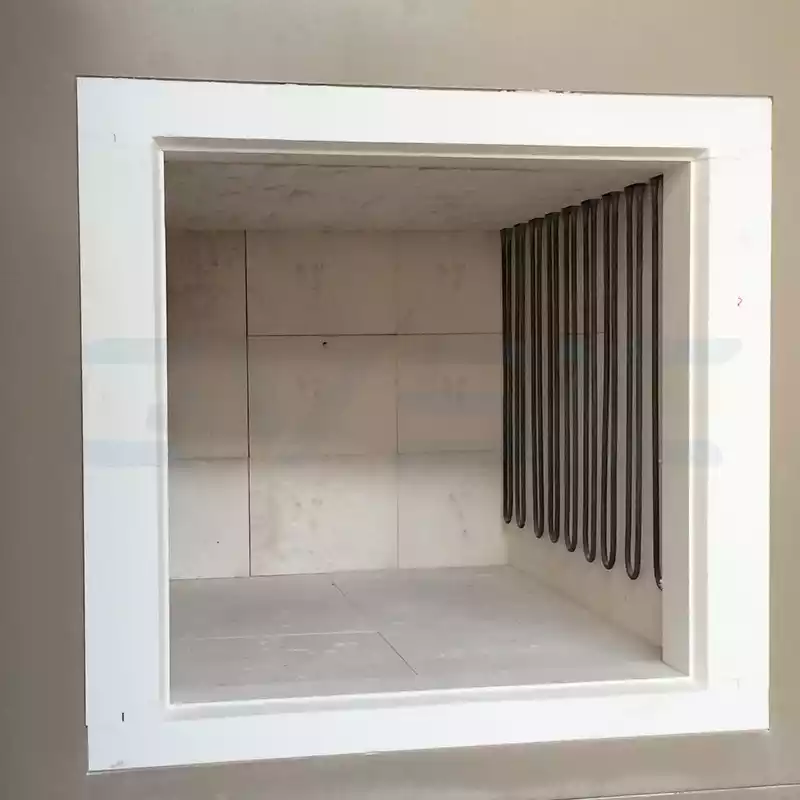
Typically, these furnaces feature MoSi2 heating elements paired with high-purity alumina/zirconia composite fiber chambers, ensuring sustained operation in oxidative or inert atmospheres.
Core Components of the 1800°C Muffle Furnace Heating System
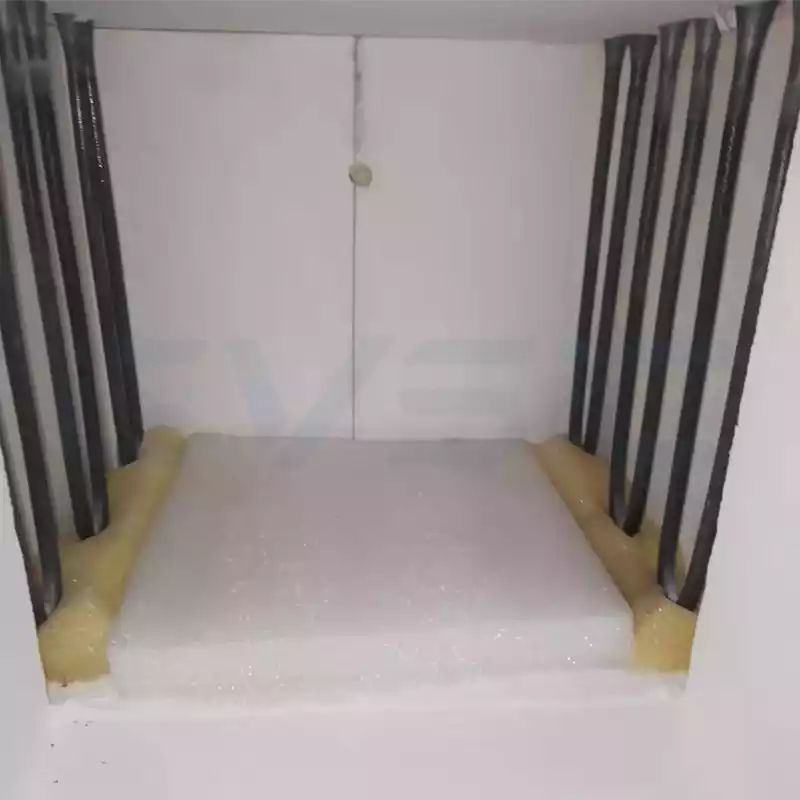
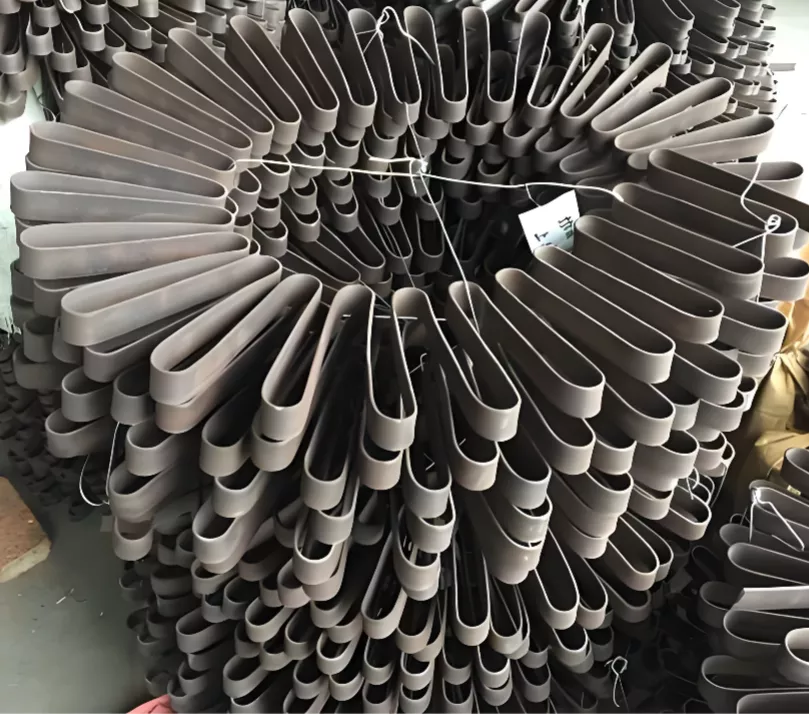
- Heating Elements: Molybdenum disilicide rods, designed for prolonged air exposure with exceptional oxidation resistance.
- Chamber Lining: High-purity alumina or zirconia fibers, rated to 1900°C for outstanding thermal insulation.
- Insulation Design: Multi-layered composites with precise inner-wall temperature gradients.
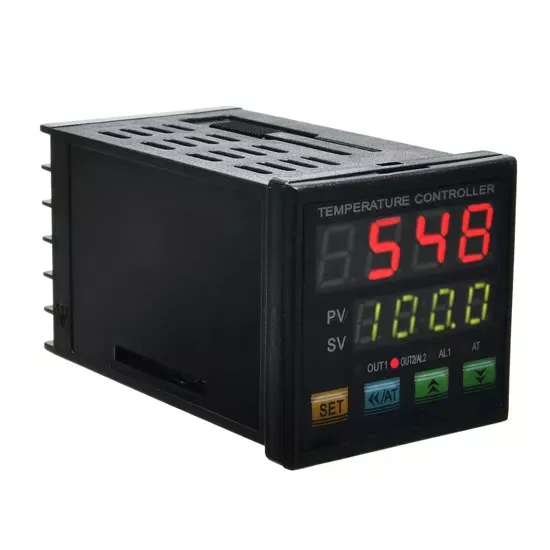
- Temperature Control: PID or advanced modular systems, delivering ±1°C accuracy.
- Heating Rates: Standard 10–30°C/min, with programmable ramp profiles for flexibility.
At 1800°C, heat transfer is dominated by radiation. This places strict demands on element durability and chamber reflectivity. Only premium MoSi2-equipped models deliver consistent, long-term reliability.
So, which materials does a 1800°C muffle furnace sinter effectively, and what processes does it support? A detailed look at these material categories and associated processes follows.

Materials Ideal for Sintering
The 1800°C muffle furnace works best with substances that have high melting points and superior thermal resistance. It excels in producing results across these categories:
High-Temperature Ceramics
- Zirconia (ZrO₂): Sinter at 1600–1800°C for robust, wear-resistant parts like dental prosthetics or industrial blades. Full densification in a 1800°C furnace boosts hardness and fracture toughness.
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): Target 1700–1800°C for structural components such as bearings or turbine blades. CVSIC’s models include inert gas capabilities to safeguard against oxidation.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Requires >1700°C for corrosion-resistant seals and tools, promoting dense grain interlocks at elevated temperatures.
- Advanced Alumina (Al2O3): Most grades operate at 1400°C, but high-purity or nanoscale grades require 1700–1800°C for best performance. High-temperature sintering reduces porosity to below 1%, thereby greatly improving mechanical properties. For example, CVSIC’s 1800°C furnace helped a ceramics lab reach 99.5% zirconia density, outperforming 1400°C systems.
Glass Materials
- High-Melting-Point Glasses: Borosilicate or quartz (SiO₂) with softening points of 1600–1700°C benefit from melting, shaping, and annealing in a 1800°C furnace for uniform clarity and homogeneity.
- Specialty Glasses: Optical or laser variants undergo stress-relief treatments to maintain precision.
Special Alloys and Metals
- Titanium Alloys: Anneal at 1600–1800°C to refine microstructures, improving corrosion resistance and strength for aerospace applications.
- Refractory Metals: Tungsten or molybdenum (melting points well above 1800°C) undergo precursor sintering or heat treatment near 1700°C for electrodes and dies in the muffle furnace.
- Metal Matrix Composites: Carbide-reinforced alloys need high temperatures to bond the matrix and reinforcements.
Note: For metals, use inert or vacuum atmospheres. CVSIC’s 1800°C furnaces let you control these settings to prevent oxidation.
Advanced Composites
- Carbon/Carbon Composites: Sinter at 1700–1800°C to strengthen fiber-matrix interfaces, ideal for aerospace heat shields.
- Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs): SiC/SiC systems achieve enhanced thermal and mechanical integrity at 1800°C.
With these examples in mind, it becomes clear that the 1800°C muffle furnace serves a broad range of high-melting-point ceramics and functional materials, making it a staple for R&D labs and cutting-edge manufacturers.
Key Process Applications
Ceramic Densification Sintering
- Promotes particle diffusion for high density and minimal porosity.
- Tailored ramp rates and dwell times refine grain size.
- ±1°C precision minimizes warping or cracks.
- Proven for alumina, zirconia, and silicon nitride.
Proven Results: Alumina density rises >10% post-1700°C sintering; zirconia peaks in toughness at 1780°C.
Powder Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
- Pre-sinters or densifies refractory powders like W or Mo.
- Advances in novel composites, e.g., Mo-Si alloys.
- Enables diffusion and recrystallization in Ar/N₂ atmospheres.
Note: Above 1700°C, inter-particle diffusion accelerates, with grain boundary mobility increasing by approximately 30%—crucial for pressureless densification in muffle furnace applications.
Crystal and Functional Material Synthesis
- Facilitates sintering and phase shifts in mono- or polycrystalline forms.
- Supports PZT piezoelectrics, YSZ electrolytes, and oxide superconductors.
- Simulates process conditions for validation testing.
Lab Favorite: Sintering PZT at 1750°C leads to full phase transitions and higher piezoelectric coefficients.
Glass, Glaze, and High-Temperature Reactions
- Conducts glass melting trials.
- Validates glaze reactivity.
- Explores oxidation or carbiding under heat.
High-Temperature Material Characterization
- Determines phase transitions (e.g., Al₂O₃).
- Measures thermal expansion.
- Assesses long-term stability.
Industries Served by 1800°C Muffle Furnaces
| Industry Sector | Key Applications |
| R&D Labs & Universities | Materials science, high-temp chemistry, functional ceramics |
| Ceramics & Powder Metallurgy | Densification, quality assurance |
| Electronics & Energy | Electrolytes, semiconductor ceramics, electrodes |
| Glass & Advanced Materials | Melting optimization, formulation tweaks |
| Aerospace & Defense | Structural ceramics, thermal barriers |
In Summary: The 1800°C muffle furnace drives research progress and supports production at scale.
CVSIC 1800°C High-Temperature Muffle Furnace for Sale
Selection and Best Practices
Before investing in a 1800°C muffle furnace, consider these factors:
Material Compatibility:
- Oxide ceramics: Air atmospheres suffice.
- Non-oxides or metals: Opt for inert/vacuum setups.
Temperature Needs:
- For sustained holds ≥1700°C, this model is indispensable.
Control Features:
- Choose PID with fuzzy logic for multi-segment programming and curve customization.
Chamber Capacity:
- Lab-scale: 1–10 L; Production: 100–1000 L.
Customization Options:
- CVSIC offers tailored chamber sizes, zone setups, and controls. Options include logos, color, and interface branding.
Final Thoughts: 1800°C—Where Technology Meets Reliability
Far more than a benchmark, 1800°C signifies:
- Peak integration of structure, controls, and elements for extreme processes.
- Unlocked potential in materials R&D and ceramics scaling for denser, more predictable outcomes.
- A hallmark of engineering excellence for leading brands.
Drawing on years of high-temperature experience, CVSIC equips global partners from lab prototypes to full production. The 1800°C solutions include OEM/ODM, chamber upgrades, and multi-zone innovations.
FAQ
How does a 1800°C furnace differ from a 1700°C model?
Beyond the temperature edge, it offers greater thermal headroom in the chamber and elements, enabling reliable extended runs.
Is silicon nitride sintering feasible?
Absolutely—pair with inert atmospheres to avert Si₃N₄ oxidation.
Vacuum compatibility?
Standard units handle oxidative environments; add sealed chambers and gas purging for vacuum needs.