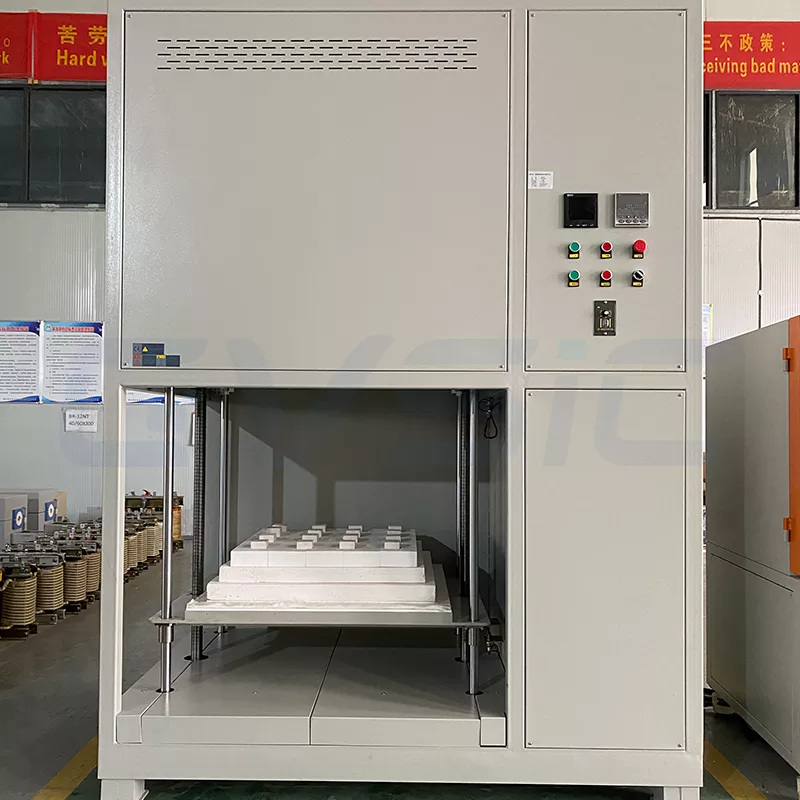
As an engineer, I know the importance of choosing the right atmosphere furnace. Box, tube, and external-heating furnaces offer unique strengths, but customers ask: What sets them apart? Which suits my needs? CVSIC presents a clear comparison guide. We’ll review features, pros, cons, and best uses for each type to help you find your high-temperature partner.

What is an Atmosphere Furnace?
An atmosphere furnace precisely controls the internal gas (hydrogen, nitrogen, argon) for high-temperature processing. Common in powder metallurgy, ceramic sintering, and metal treatment, each furnace type has a unique chamber design, heating method, and uses. Next, we’ll compare three types: chamber, tube, and external heating furnaces.
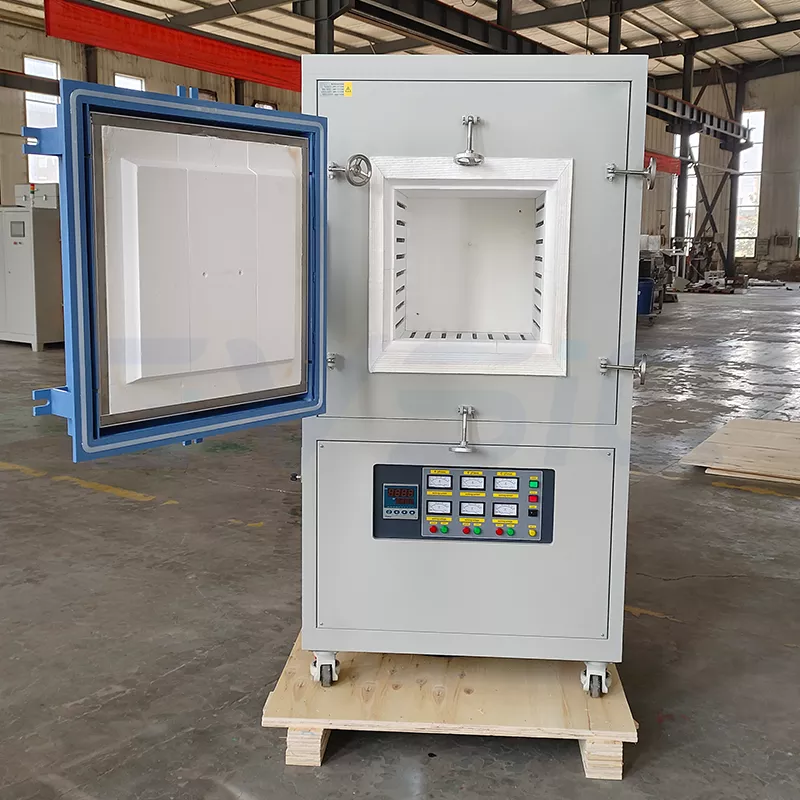
1. Atmosphere Box Furnace: The Flexible “All-Rounder”
Features:
A Box atmosphere furnace utilizes a sealed cubic or rectangular compartment, similar to a “high-temperature box.” It suits regular-shaped workpieces, provides easy operation, and is commonly used in laboratories and small to medium-sized production settings.
Advantages:
- User-friendly operation: Spacious chamber allows easy loading/unloading of workpieces and accommodates samples of various shapes and sizes.
- Temperature uniformity: Multi-zone heating design ensures stable and consistent temperatures throughout the chamber, perfectly suited for processes demanding high temperature uniformity.
- Flexibility: Supports multiple protective gases (e.g., hydrogen, nitrogen) to accommodate diverse process requirements.
- Cost-effective: Lower initial investment and maintenance costs compared to other furnace types.
Disadvantages:
- Limited capacity: Relatively constrained chamber size cannot accommodate oversized workpieces or high-volume production demands.
- Slower heating rates: May be slightly slower than tube furnaces.
Applications:
- Laboratory R&D: Ceramic sintering tests, alloy performance evaluations, etc.
- Small-batch production: Sintering of carbide tools, stainless steel components, etc.
- Education and experimentation: Small-scale process validation in universities or research institutions.
CVSIC Tip:
The CVSIC Box atmosphere furnace features high-precision PLC control, maintaining temperature deviation within ±2°C. Equipped with a multi-gas circuit system, it perfectly meets the diverse needs of laboratories and small-scale production.
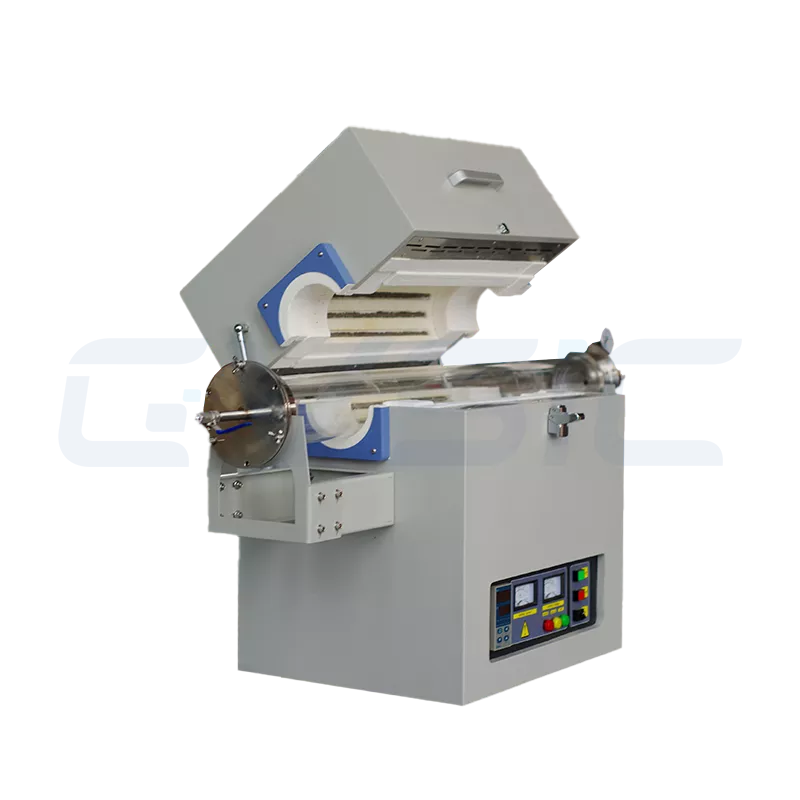
2. Tube Atmosphere Furnace: The Precision “Experiment Expert”
Features:
The Tube Atmosphere Furnace is a slender tube with external heating elements, ideal for small or elongated workpieces. Its design focuses on gas flow and experimental flexibility, making it a staple in the lab.

Advantages:
- High-Precision Control: The tubular furnace ensures uniform gas distribution and exceptional atmosphere control accuracy, ideal for demanding experiments.
- Rapid Heating: The compact furnace chamber achieves fast temperature ramps, meeting processes requiring swift thermal transitions.
- Exceptional Flexibility: Supports diverse gas atmospheres and complex temperature profiles, providing ample room for R&D exploration.
- Compact footprint: Compact design suits laboratories with limited space.
Disadvantages:
- Limited capacity: The tube furnace chamber size restricts the processing of large workpieces or batch production.
- Workpiece limitations: Better suited for slender or small samples; unsuitable for complex-shaped workpieces.
Applications:
- New material R&D: e.g., nanomaterial preparation, graphene synthesis, catalyst development.
- Small-scale sintering: Experimental sintering of ceramic or metal powders.
- University laboratories: Teaching demonstrations or fundamental research experiments.
CVSIC Tip:
CVSIC tube furnaces feature optimized gas flow structures with flexible multi-gas switching, ideal for high-precision experiments. Our engineers also offer custom tube designs tailored to your sample dimensions!
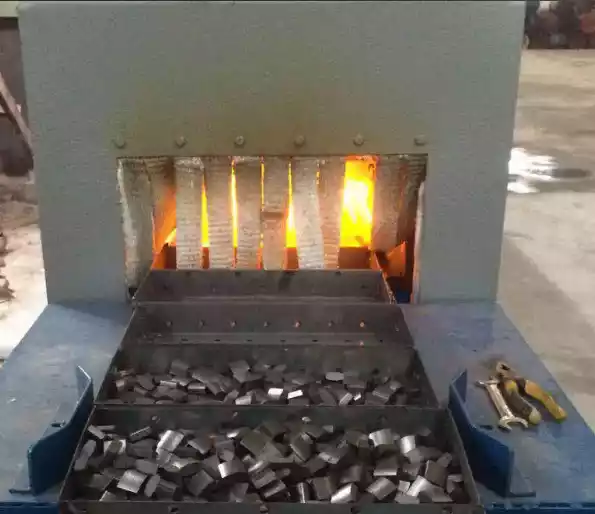
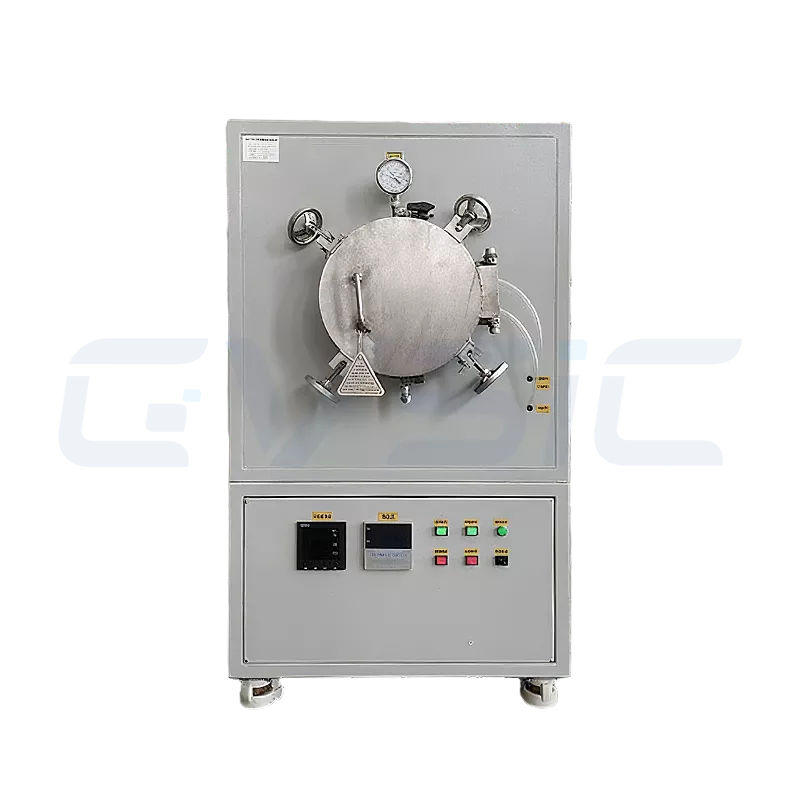
3. External-Heat Atmosphere Furnace: The Hardcore Player in Ultra-High Temperatures
Features:
External heating elements sit outside the furnace chamber, radiating heat inside. This design is suitable for ultra-high temperatures (greater than 1600°C) or environments with controlled atmospheres. Minimizing contact between heating elements and protective gases extends equipment life.

Advantages:
- Ultra-high temperature capability: Reaches temperatures exceeding 1800°C, suitable for processes like high-temperature ceramic sintering or special alloy treatment.
- Durable: Isolated heating elements prevent corrosion, extending lifespan.
- High atmosphere purity: Ideal for processes demanding extremely stringent atmosphere conditions, such as semiconductor material preparation in argon environments.
- Large-Capacity Options: Supports custom large-chamber designs for industrial-scale production applications.
Disadvantages:
- High Cost: Complex equipment structure results in higher initial procurement and maintenance expenses.
- lower Heating Rate: Limited by external heating methods, the heating speed is slower than that of tube furnaces.
- Higher Energy Consumption: Ultra-high-temperature operation typically requires greater electrical power consumption.
Applications:
- High-temperature ceramic sintering: Processing of high-performance ceramics like zirconia and silicon carbide.
- Special material preparation: Frontier fields such as high-temperature superconductor R&D and semiconductor crystal growth.
- Industrial high-end applications: Precision heat treatment of critical materials in aerospace and other sectors.
CVSIC Tip:
CVSIC’s retort atmosphere furnaces are constructed with high-performance refractory materials and equipped with intelligent temperature control systems, ensuring stability and safety even at extremely high temperatures—ideal for high-end manufacturing processes.
How to Select the Right Atmosphere Furnace for You?
Consider these five factors when choosing an atmosphere furnace:
Workpiece Size & Volume:
For small samples or batches, use box or tube furnaces.
For large or mass production, try external heating or custom furnaces.
Temperature Requirements
Conventional sintering (<1400°C): Choose box or tube furnaces.
Ultra-high temperatures (>1600°C): Opt for external heating furnaces.
Atmosphere Control
Laboratory R&D: Prioritize high atmosphere precision—tube furnaces excel.
Industrial production: Emphasize stability—box or external heating furnaces are more suitable.
Budget & Energy
Box and tube furnaces are lower cost, fitting labs and SMEs.
External heating suits large budgets and advanced needs.
Safety:
When using flammable gases like hydrogen, ensure equipment has comprehensive safety systems.
Real-world Case:
A client developing novel ceramic materials used CVSIC’s tube atmosphere furnace to test multiple gas mixtures, rapidly identifying optimal process parameters. Upon scaling production, they purchased CVSIC’s chamber furnace, achieving a 97% yield rate. For clients requiring ultra-high-temperature sintering, we recommend an external heating furnace, which has successfully enabled the production of aerospace-grade ceramic components. This experience highlights the importance of selecting the right furnace type, as it significantly enhances process efficiency and product quality.
Why Choose CVSIC?
CVSIC furnaces are partners in success. With over 20 years of expertise, we understand all types of furnaces. We offer options from lab to industrial scale. Whether chamber adaptability, tube precision, or external furnace capability, CVSIC customizes solutions for you.
Still unsure about which type of furnace to choose? Contact CVSIC’s engineering team today for a free consultation. We’ll help you find the perfect solution!
FAQ
Which is better for labs: chamber or tube atmosphere furnaces?
Tube furnaces excel at experiments requiring high-precision atmosphere control and rapid heating. Chamber furnaces are ideal for larger samples or small-batch production. CVSIC can recommend the optimal model based on your specific needs.
Why are externally heated furnaces suitable for ultra-high-temperature processes?
External heating elements are completely isolated from the atmosphere, offering high-temperature resistance and extended lifespan. They are ideal for sintering ceramics or specialty materials at temperatures exceeding 1600°C.
How do the safety features differ across the three furnace types?
Chamber and tube furnaces feature relatively simple structures with higher safety levels, accommodating various gas types. Externally heated furnaces require stricter safety protocols due to their high-temperature characteristics and complex design. All CVSIC furnace models incorporate multiple safety protection systems to ensure operational security.
How can the atmosphere furnace operating costs be reduced?
Prioritize energy-efficient furnace types (such as CVSIC’s chamber or tube furnaces), optimize gas flow control, and perform regular equipment maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Our furnace models achieve energy consumption 15% lower than industry averages, delivering fundamental cost savings.
Can CVSIC customize different types of atmosphere furnaces?
Absolutely! CVSIC offers full-scale customization from furnace chamber dimensions to atmosphere systems, meeting diverse needs from laboratory to industrial applications. Feel free to inquire anytime!