For many procurement engineers, “How to pick a ceramic fiber board?” seems like a straightforward question, but when it hits your project, you’ll spot:
- Two boards rated at 1260℃ can vary in price by 40%.
- Same 50mm thickness—some turn to powder after six months, others last 3 years.
- Some boards snap easily during installation and warp under heat; others stay rock solid.
- Claimed “density 300kg/m³” versus “actual only 240kg/m³” is a huge gap.
- Pick the wrong high-temp board, and your furnace door seals or flame-contact spots go wrong, too.
I’ve seen plenty of on-site disasters from bad ceramic fiber board choices: furnace walls falling off, uneven electric furnace heating, energy costs shooting up, insulation layers caving in… Almost always ’cause folks “didn’t think it all through when picking the board.”
Picking ceramic fiber boards ain’t just about skimming specs—it straight-up affects if your gear runs steady, saves bucks, and skips hassles.

Today, from CVSIC, we’re covering the four big ones everyone asks about: density, thickness, heat resistance, and strength. We’ll show how to weigh ’em in real scenarios to grab the right ceramic fiber board for you.
The Four Core Factors Shaping Ceramic Fiber Board Picks
A ceramic fiber board is basically a “heat shield” for high temps—it blocks heat, takes vibrations, fights corrosion, and installs easily.
Picking ceramic fiber boards boils down to four key things:
- Density: Affects weight and insulation, sets strength, lifespan, and scour resistance.
- Thickness: Sets insulation performance and structural needs.
- Heat Resistance Level: 1050℃ / 1260℃ / 1400℃ / 1600℃.
- Strength and Process Type: Wet-formed / Vacuum-formed / Reinforced.
These ain’t standalone—for example, high-density boards are tough but heavy, perfect for load-bearing spots; low-density ones are light but weaker, so beef ’em up with thicker boards.
When picking, ask yourself: What’s your ambient temp? Any vibrations or corrosion? Budget and space limits? Answer those to skip the “bought fancy but used it wrong” awkwardness.
Below, I’ll break it down with my real-world experience and common picks from actual engineering jobs.
How to Pick Ceramic Fiber Board Density: The Key to Structural Strength and Longevity
Common densities for ceramic fiber boards out there:
| Board Density | Common Range | Applicable Scenarios | Engineer Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 260–300 kg/m³ | Ordinary Board | Backing layer, non-structural parts | Cheap, but not resistant to erosion, prone to powdering |
| 350–400 kg/m³ | Conventional High-Strength Board | Furnace door, furnace wall, hot air duct | Significantly better stability under working conditions, highest cost-effectiveness |
| 450–500 kg/m³ | Ultra-Strong Board | Directly facing flames, tuyere area, fluid erosion surfaces | Suitable for high wind speed and high thermal shock areas |
| 600+ kg/m³ | Special Board | Vacuum furnace fixtures, equipment support pads | High strength but expensive, for specific uses |
Why’s density a big deal?
Density calls the shots on:
- If the board’s strength handles mechanical stress
- If scour resistance (from flames, wind) holds up
- If it’ll bend or sag at high temps
- If the lifespan goes beyond a year
Pro tips (CVSIC engineer):
- No loads, no direct fire: 300 kg/m³ gets it done.
- Doors, walls, heat zones: ≥350 kg/m³
- Straight flame hits, high-flow vents: 450–500 kg/m³
- In stressed areas, low-density boards can fall apart under vibration.
- At 800°C, mid-density boards lose 5% less heat than low-density ones but have 30% more strength.
- Bump density by 100 kg/m³, costs go up roughly 15%
Density’s prime for skimping, so always check the real density test report when buying.

How to Choose Ceramic Fiber Board Thickness?
Usual thicknesses: 20mm / 25mm / 30mm / 40mm / 50mm / 60mm / 75mm / 100mm
Pick thickness by three things:
Heat loss needs at your target temp
Say furnace inside at 1200℃, aiming for outer surface 60–80℃—common setups:
- 30mm board + 50mm blanket → Lightweight furnaces
- 50mm board + 50–100mm blanket → Industrial ones
- 75–100mm board (layered) → Heat-treat or electric furnaces
Space constraints
Many electric furnaces are cramped, so often:
- 25mm board + blanket
- 30mm reinforced board
If the work surface takes mechanical loads
like:
- Hot-press pads → 40–60mm
- Glass annealing → 20–30mm
- Vacuum furnace supports → 60–75mm reinforced.
CVSIC insights:
- Thin boards (<25mm) flex for installs, heat quickly, fit tight spaces or quick patches.
- Thick ones (>50mm) insulate deeper and cut thermal bridges, but they’re heavy and costly—layer ’em to stop sagging.
- Too thin? Heat shoots through, energy down the drain.
- Too thick? Eats space, adds extra costs.
Pro trick: Estimate with heat balance formula—thickness = (temp diff × area × time) / (conductivity × efficiency goal). In short, over 1000°C? Start at 25mm; extreme shocks? Up to 75mm.
Bottom line, thicker isn’t always better—it’s about thermal needs plus structure.
How to Pick the Heat Resistance Level?
Standard heat levels for ceramic fiber boards:
Level Continuous Use Temp Usage Tips
| Grade | Continuous Use Temperature | Usage Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| 1050℃ (Ordinary Board) | 950–1000℃ | Only suitable for low-temperature furnaces, backing layers |
| 1260℃ (High-Temperature Board) | 1100–1150℃ | Commonly used, high cost-effectiveness |
| 1400℃ (High-Alumina Board) | 1250–1350℃ | Metallurgy, ceramic kiln hot surface layer |
| 1600℃ (Zirconium-Containing Board) | 1400–1500℃ | High-temperature conditions, vacuum furnaces, flame contact areas |
How to choose?
Furnace temp minus 100℃ ≈ board’s “safe steady temp.”
Check peaks and steadies first; lots of intermittent shocks? Level up for buffer. Chem corrosion (like alkali fumes)? Pick high-alumina or zirconia ceramic fiber boards.
For your max furnace temp:
- 1100℃ → 1260℃ board
- 1250℃ → 1400℃ board
- 1400–1500℃ → 1600℃ zirconia board
Don’t skip preheating: Ramp new boards slowly to dodge early cracks. Prioritize app fit—metallurgy? 1400°C; ceramic kilns? 1260°C does it, save cash for strength.
Steer clear:
“1200℃ furnace with 1050℃ board”—too many wrecks like that.

How to Choose Ceramic Fiber Board Strength?
Ceramic fiber board strength includes compressive (>0.1 MPa) and flexural. It sets anti-crush and quake-proof abilities. Low-strength? Brittle, good for still spots; high-strength (whisker-added) handles impacts, ideal for loads or vibes.
Strength depends on:
- Fiber type (basic → high-alumina → zirconia)
- Binder ratio
- Vacuum-forming
- Density
- Post-silica sol or binder boosts
Usual stats:
- Flexural strength: 0.5–1.2 MPa
- Compressive strength: 0.3–0.85 MPa
- High-temp shrink: <2–3%
Quick hits:
- Door or fire-block boards → “High-strength” types
- Direct-flame areas → “Reinforced or silica-sol boosted.”
- Vac heat-treat → “Low-shrink zirconia.”
- Support pads → Eye compressive strength, not heat
Ceramic Fiber Board Recs for Different Scenarios
Electric or Lab Furnaces
- Board: 1260℃ / 1400℃
- Density: 350–400 kg/m³
- Thickness: 20–50mm
Heat-Treat Furnaces
- Hot layer: 1400℃ high-strength
- Backing: 1260℃ basic
- Thickness: 50–100mm mix
Metallurgy Furnace Openings, Vents
- Board: 1400℃ or 1600℃
- Density: 450–500 kg/m³
- Process: Reinforced / Scour-resistant
Glass Field
- Insulation: 1260℃ board
- Support pads: 600 kg/m³ specialty
Vac Furnaces
- Low-shrink, low-impurity needs → 1600℃ zirconia board.
Tell me your exact setup, and I’ll fine-tune the suggestions (temp, wind, pressure, structure).
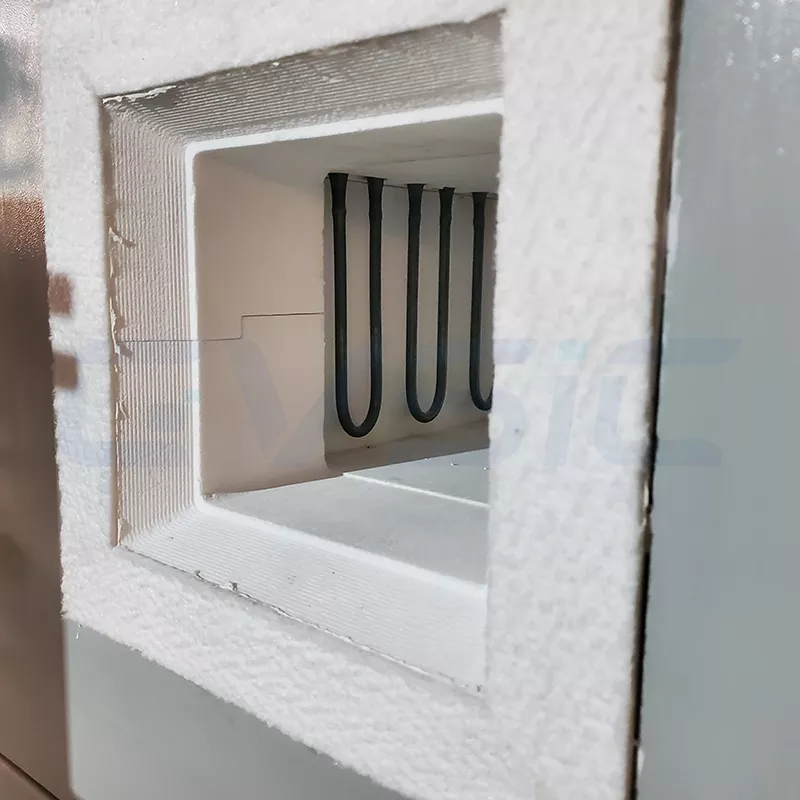

Common Goofs in Ceramic Fiber Board Picks
Goof 1: Just eye price, skip lifecycle—cheap boards uneven density, swap in six months, costs more overall. CVSIC mid-high? Solid ROI.
Goof 2: Miss the environmental factors—corrosive spots, high heat resistance is worthless; coat it properly.
Goof 3: Bulk blind buys—sample test first! Free from us.
Optimize: Layer designs (inner high-heat, outer strong), CVSIC OEM custom, quick ship.
CVSIC’s Pick and Custom Perks
As ceramic fiber makers, CVSIC delivers:
- Full density range 260–600 kg/m³ boards
- Tiered heat boards: 1050/1260/1400/1600℃
- Custom big sizes (1200×2400mm / 1220×2440mm)
- CNC cuts, tolerances under ±1mm
- Silica-sol boosts, scour/water resists
- OEM/ODM, private labels, custom packs
- Free engineer pick help.
Share your setup, get full pick and material plans.
Picking ceramic fiber boards is like choosing teammates—they gotta be reliable and tough. Light or heavy density, thin or thick, heat baseline, strength grit—nail these, ops go smoother. CVSIC ain’t just suppliers; we’re partners, with full support from picks to after-sales.
Ceramic Fiber Board Pick Questions
Is higher board density better?
Nah. Boosts strength, but ups cost and load. Match to job needs.
Board heat rating the same as steady use temp?
Nope. Rated is peak; steady’s usually 100–150℃ lower.
Direct flame okay?
Not for basics. Pick high-strength or zirconia.
Replace refractory bricks?
Yeah, in light, quick-heat, efficient furnaces—but with design backup.
Dust from boards?
During cuts, yeah—wear gear; after, minimal, stays stable.