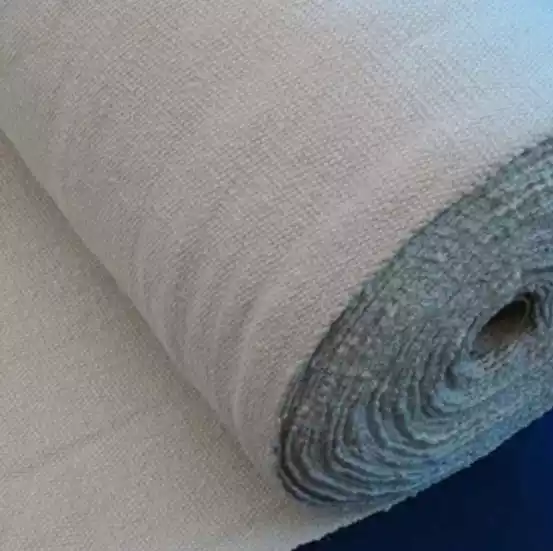
In high-temperature industries, lightweight, efficient, and energy-saving insulation provides a key competitive advantage. Ceramic fibre is essential in achieving this.
As a high-temperature industrial engineer, I understand the crucial role ceramic fibre plays in efficient equipment operation and energy conservation. CVSIC is devoted to providing high-quality ceramic fibre products. This guide explores the performance, applications, and selection tips for ceramic fibre, helping you avoid common pitfalls—whether you’re new to the field or an experienced expert.
What is ceramic fibre?
Ceramic fibre, also known as high-temperature glass wool or refractory fibre, is a lightweight refractory material made from high-purity alumina and silica through melt spinning or centrifugal spinning processes.
Its core advantages include:
- Ultra-high temperature resistance: Conventional products can operate at temperatures between 1000°C and 1430°C;
- Extremely low thermal conductivity: Excellent insulation properties significantly reduce heat loss;
- Lightweight and flexible: Lighter and more flexible than traditional refractory bricks or calcium silicate materials;
- Easy to install: Can be cut, joined, or customised to fit various equipment structures;
- Strong thermal shock resistance: Suitable for frequent start-stop furnace operations.
It is recognized for superior temperature resistance, low thermal conductivity, and thermal shock resistance, and is often used in industrial furnaces, heat treatment equipment, and pipeline insulation. Think of it as a ‘fireproof cloak’ that protects equipment and reduces energy consumption.
CVSIC’s ceramic fibre products are precisely designed to meet various high-temperature requirements ranging from 1000°C to 1800°C. Whether you need to protect equipment, improve efficiency, or reduce maintenance costs, ceramic fibre can be your reliable partner.
Classification and Common Types
Ceramic fiber products come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications. Below are the primary types offered by CVSIC, along with their typical uses:
| Type | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
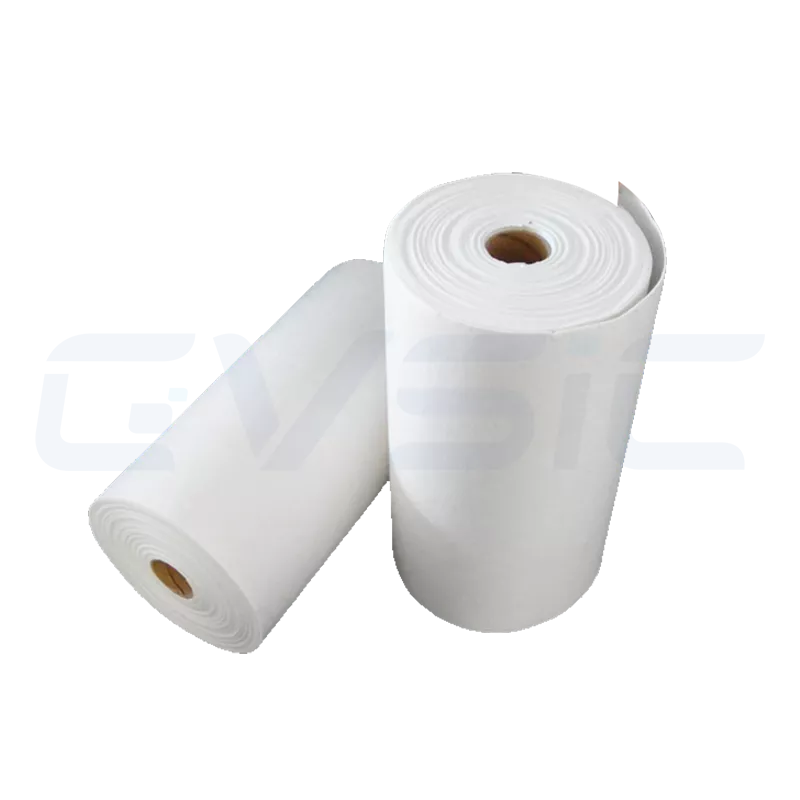
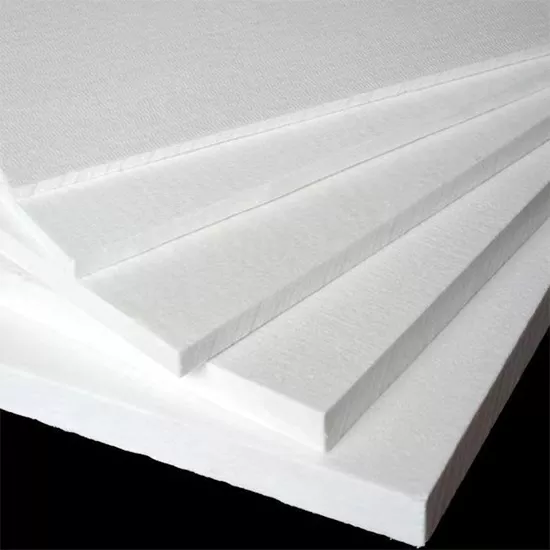
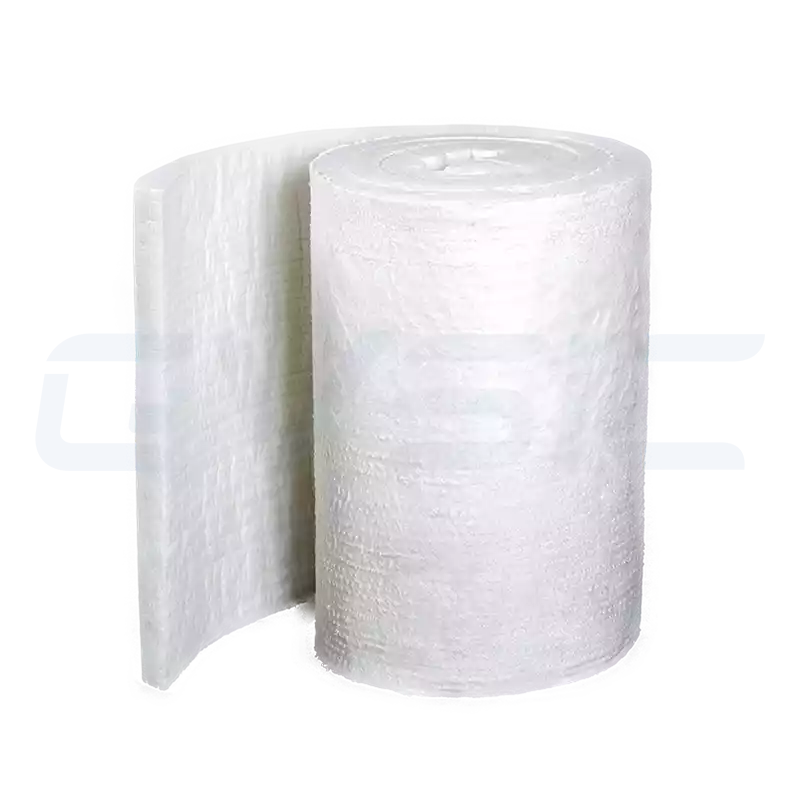
| Ceramic Fiber Blanket | The most common flexible material, supplied in rolls, lightweight and easy to install | Industrial furnace wall linings, furnace door seals, high-temperature pipeline insulation |
| Ceramic Fiber Board | Produced via wet vacuum forming, offering enhanced rigidity | Hot face contact areas, hot air ducts, heat insulation baffles |
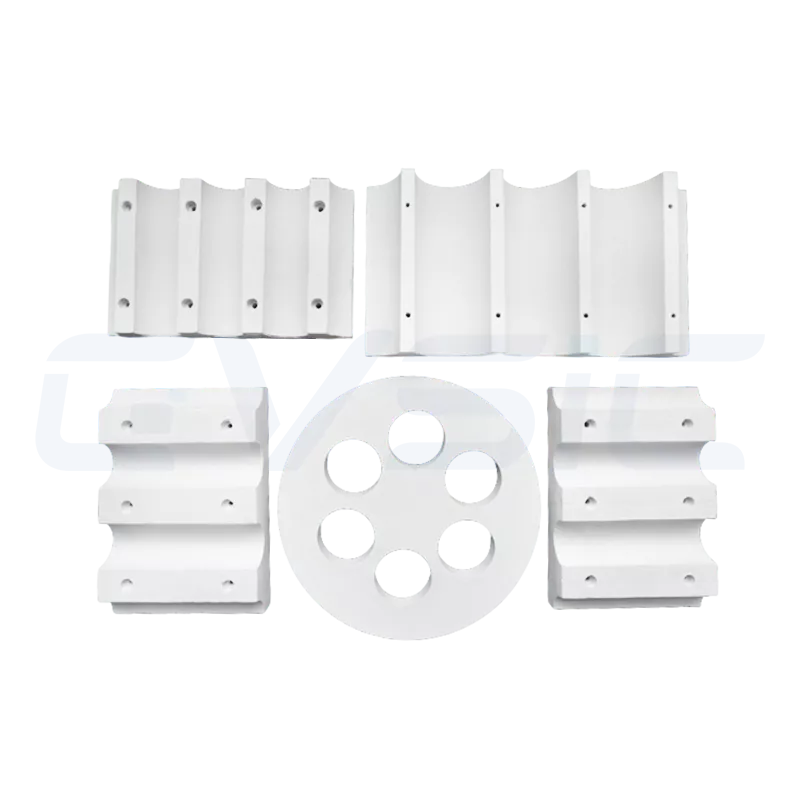
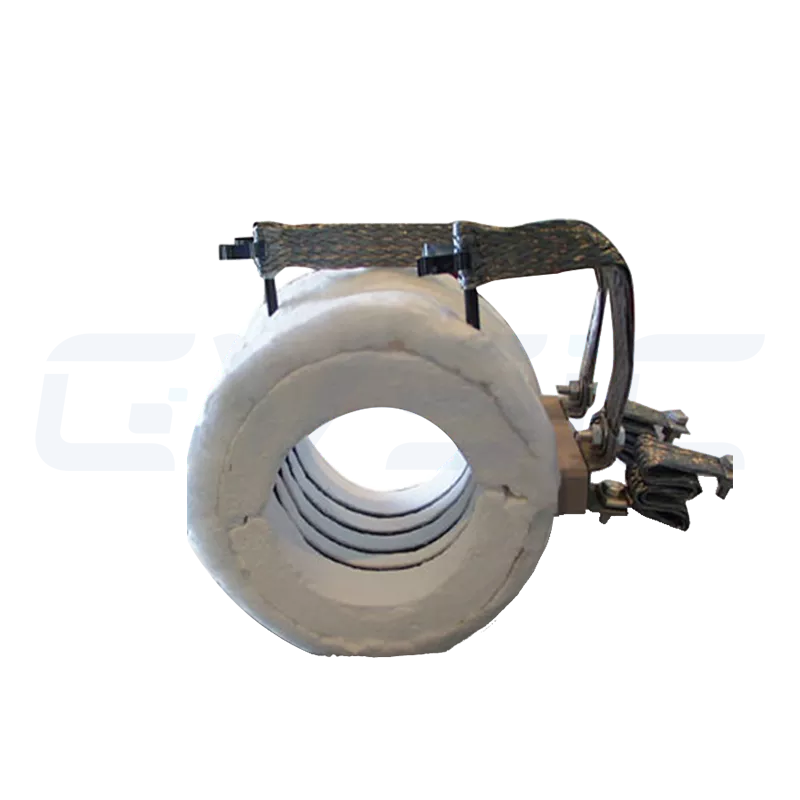
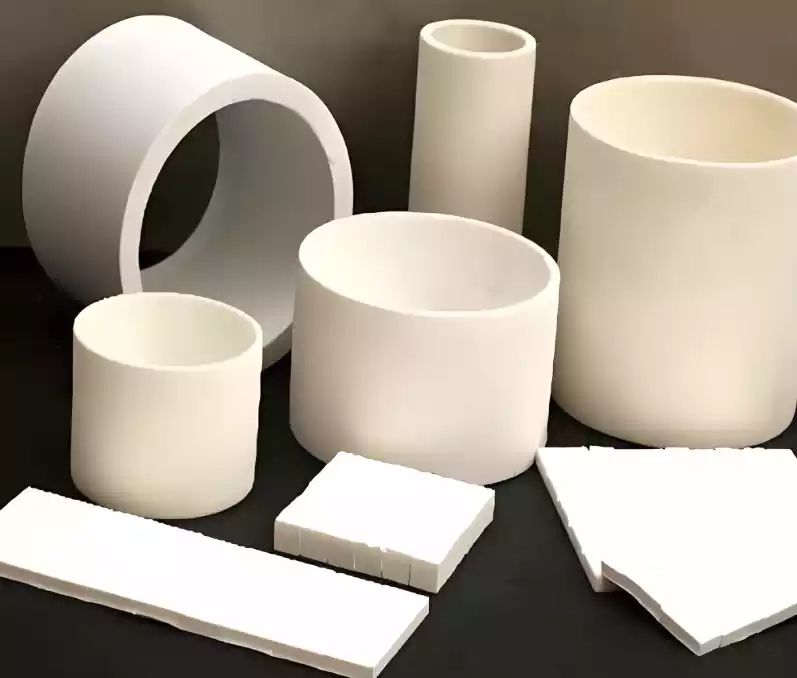
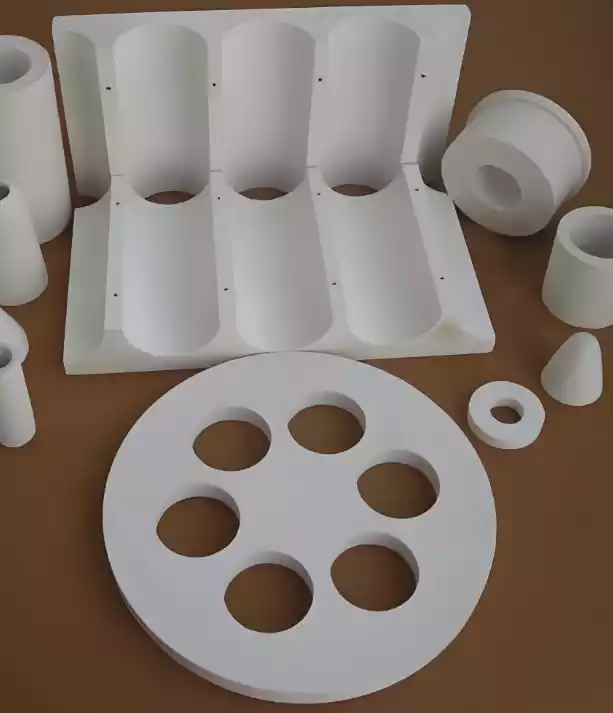
| Ceramic Fiber Module | Compressed and folded fiber blankets formed into pre-fabricated blocks | Large industrial furnace lining systems (e.g., steel and glass industries) |
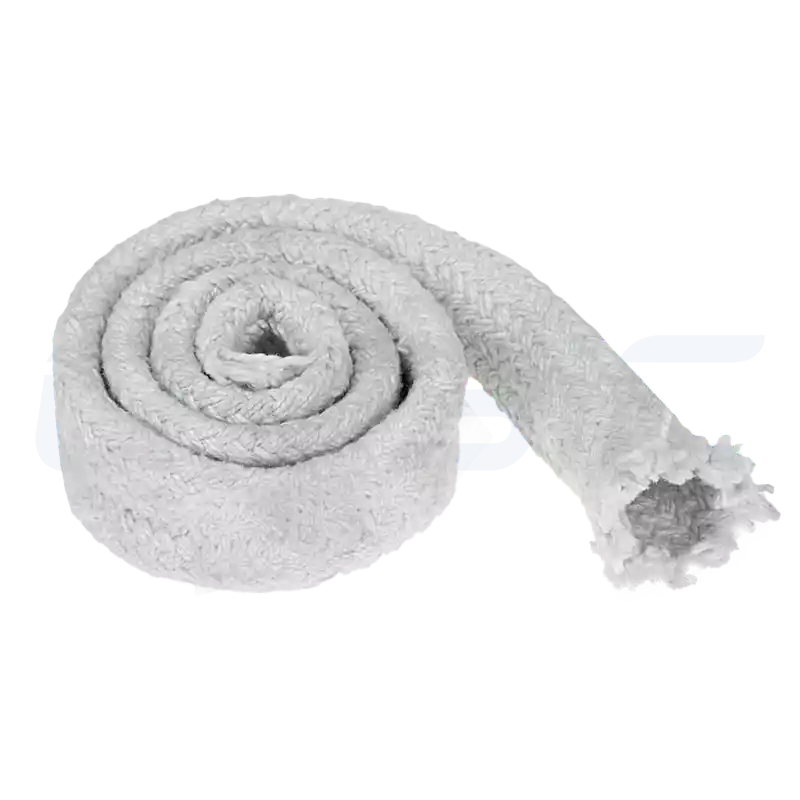
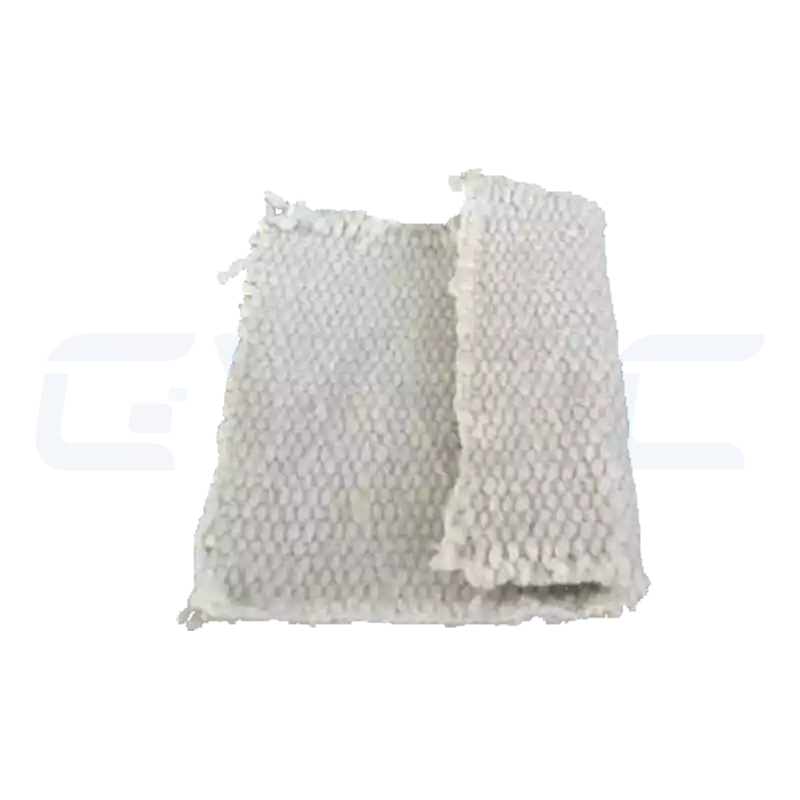
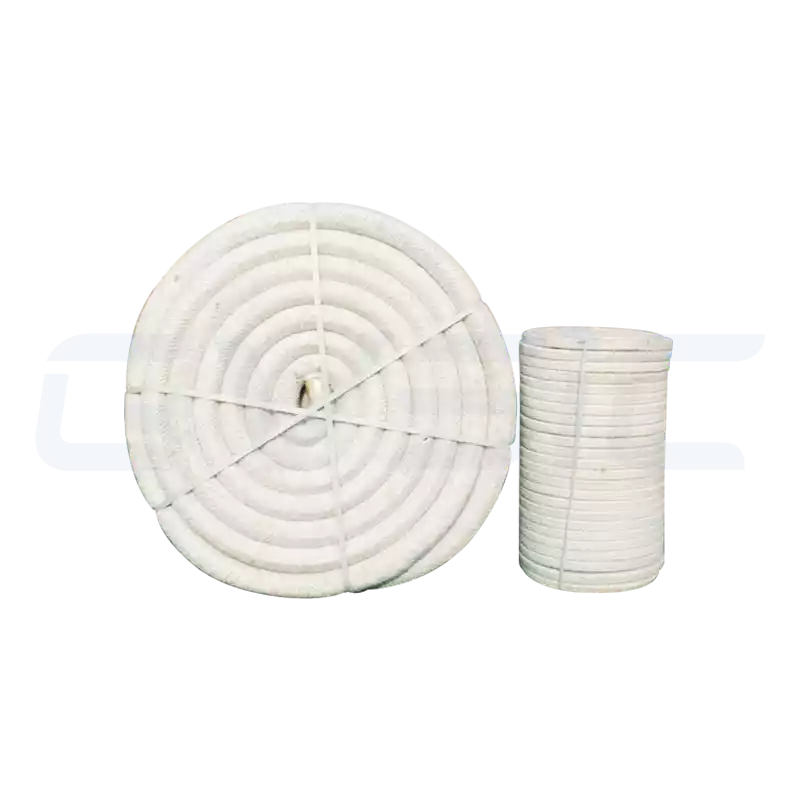
| Ceramic Fiber Paper/Cloth/Rope | Ultra-thin, flexible, ideal for sewing or sealing applications | Expansion joint seals, thermocouple protection, furnace door sealing strips |
Each type undergoes CVSIC’s rigorous quality control to ensure peak performance in its designated application.

Manufacturing Process Overview
The manufacturing process of ceramic fibre is like a ‘high-temperature magic show.’ The raw materials are processed to produce ceramic fibre products, and the manufacturing process is closely related to product performance. The main processes include:
- Spun Type: Longer fibres with good flexibility and high tensile strength, suitable for areas requiring high mechanical strength;
- Blown Type: Finer fibres with better thermal insulation properties, commonly used in insulation layers;
- Vacuum Forming: Used to manufacture shaped products such as panels and custom components, offering excellent dimensional stability and resistance to wind erosion.
Raw materials (such as high-purity alumina and silica) are melted at high temperatures, then processed into fine fibres via the above methods, and subsequently formed into blankets, panels, or modules. CVSIC employs advanced production processes to ensure uniform fibre distribution, controllable density, and minimal impurities, thereby enhancing product durability.
Our engineering team recognizes that manufacturing processes have a direct impact on product performance. Therefore, CVSIC’s ceramic fibres not only withstand high temperatures but also maintain stability in harsh environments, giving your equipment an edge.
Performance Characteristics
The appeal of ceramic fibres lies in their multiple advantages. Here are several key characteristics:
- High-temperature resistance: Can withstand temperatures ranging from 1000°C to 1800°C, with some products suitable for ultra-high-temperature environments.
- Low thermal conductivity: At 1000°C, thermal conductivity is typically ≤0.25 W/m·K; significantly superior to traditional materials such as refractory bricks, rock wool, and calcium silicate boards.
- Thermal shock resistance: Ceramic fibre remains stable under rapid temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking.
- Lightweight: Density is approximately 1/5 that of traditional refractory bricks; reduces equipment load and saves structural costs.
- Chemical stability: Resistant to most acid and alkali corrosion, compatible with various high-temperature atmospheres, suitable for complex environments such as chemical and metallurgical industries.
These characteristics make CVSIC’s ceramic fibre products a ‘versatile performer’ in high-temperature industries. Want to know how to optimise your furnace using these characteristics? Check out our furnace insulation case studies.
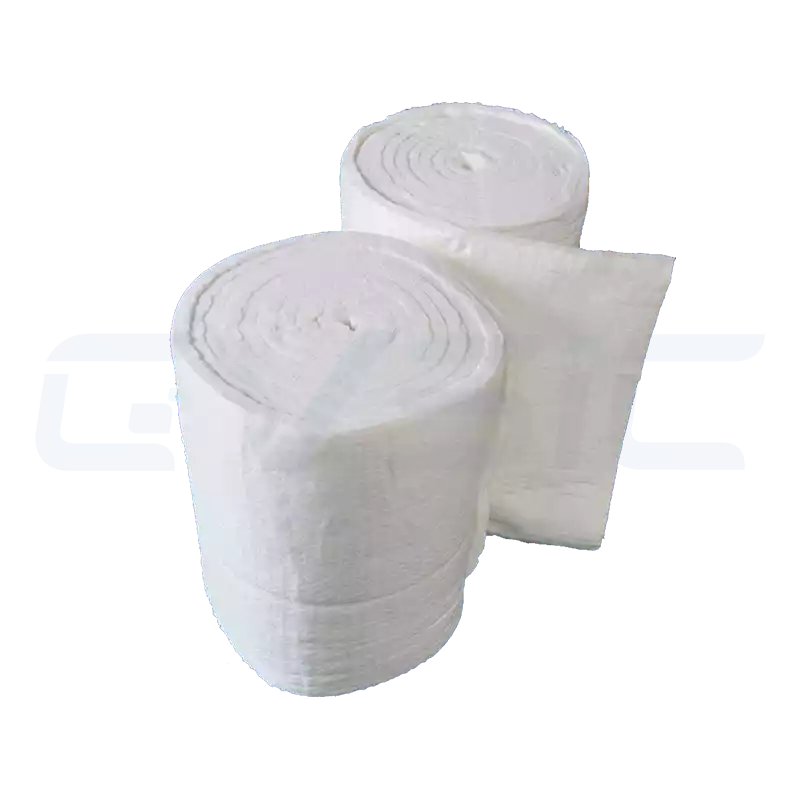

Application Industries and Scenarios
The application scope of ceramic fibre is extremely broad, covering nearly all high-temperature industrial sectors:
- Steel and Metallurgy: Used as lining for heating furnaces and homogenisation furnaces to reduce heat loss and enhance production efficiency.
- Petrochemical Industry: Pipe insulation and reactor thermal insulation to ensure safe equipment operation.
- Power industry: Insulation for boilers and flue ducts, contributing to energy conservation and emissions reduction.
- Ceramic and glass manufacturing: Lining for kilns, ensuring process stability and product quality.
- Aerospace: Used in high-temperature experimental equipment, meeting demands under extreme conditions.
Comparison with Other Refractory Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Scenarios |
| Ceramic Fiber | Lightweight, low thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistant, easy to install | Slightly lower strength, avoid mechanical impact | Furnace linings, pipeline insulation |
| Aluminum Silicate Wool | Low cost, good flexibility | Lower temperature resistance (<1200°C), prone to aging | Low-cost temporary insulation |
| Calcium Silicate Board | Strong rigidity, load-bearing | Higher thermal conductivity, inferior insulation | Heat insulation layers needing structural support |
| Traditional Refractory Bricks | High strength, durable | Heavy, complex installation, high thermal conductivity | Fixed furnace chambers with high mechanical strength |
CVSIC’s ceramic fibre offers significant advantages in terms of lightweight design, insulation performance, and ease of installation, making it particularly suitable for modern industries prioritising efficiency and energy savings.
Selection Guide: How to Choose the Right Ceramic Fibre Product
When selecting ceramic fibre products, you should consider the following key factors:
- Operating Temperature: Determine the operating temperature of your equipment and select products with matching temperature ratings. For example, CVSIC’s ceramic fibre modules can withstand temperatures up to 1600°C.
- Application Scenario: Select the appropriate form (e.g., blanket, board, or module) based on equipment type (e.g., furnaces, pipes, seals, etc.).
- Installation Environment: Consider construction space and time. Modular products are suitable for quick installation, while fibre blankets are better suited for complex shapes.
- Safety and Environmental Protection: CVSIC’s ceramic fibre products comply with international environmental standards, and some models use low-biopersistent fibres to reduce health risks.
- Budget and Performance Balance: High-performance products may be slightly more expensive, but they offer significant long-term energy-saving benefits. Our engineers can provide you with a cost-benefit analysis.
Installation Notes:
- Protective Measures: Wear gloves and a mask during installation to avoid inhaling fibres or skin irritation.
- Fixing Methods: Ensure high-temperature-resistant anchors are used to secure fibre modules or panels to prevent loosening.
- Sealing Treatment: Use ceramic fibre fabric or high-temperature sealant at joints to ensure insulation effectiveness.
Need more detailed installation guidance?
Why choose CVSIC?
At CVSIC, we do more than just provide ceramic fibre products; we offer reliable solutions. Our products undergo rigorous testing to ensure outstanding performance in extreme environments. Our team of engineers is always available to provide technical support, from product selection to installation and beyond. By choosing CVSIC, you will receive:
- High-quality products: durable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly.
- Professional support: one-on-one consultation and customised solutions.
- Global service: Quick response, covering multiple industries.
Conclusion
Ceramic fibre is the ‘unsung hero’ of high-temperature industries, and CVSIC is ready to help you realize its full potential. Ready to boost your equipment efficiency, cut energy costs, and solve your insulation challenges? Act now. Contact CVSIC today for a free consultation or sample, and let us help you achieve your industrial goals with proven ceramic fibre solutions.
FAQ
Is ceramic fibre harmful to humans?
CVSIC’s ceramic fibre products are optimised, with some using low-biopersistent fibres, and comply with strict environmental and safety standards. Proper protective measures during installation ensure safe use.
How do I determine if ceramic fibre needs replacement?
Inspect for visible wear, cracks, or reduced insulation performance. CVSIC offers free technical consultations to help assess the condition of your product.
Can ceramic fibre be used in outdoor environments?
Some products require additional waterproofing treatment. Our team can recommend solutions tailored to your specific needs and requirements.
How can I reduce installation costs for ceramic fibre?
Modular products can significantly reduce construction time. Contact CVSIC for customised recommendations!