Introduction: Efficiently Address Dental Sintering Furnace Issues for Seamless Lab Operations
Dental sintering furnaces work hard at high heat, so it’s normal for things to go wrong sometimes. If your furnace won’t heat up, the temperature isn’t stable, or the sintering results aren’t great, you’ll want to find and fix the problem quickly to keep your lab running smoothly. CVSIC will provide you with detailed guidance on how to identify issues, resolve them promptly, and extend the lifespan of your heater.

Common Faults and Troubleshooting Solutions for Dental Sintering Furnaces
Here’s a simple breakdown of common problems you might run into, what causes them, and what you can do to fix them—covering everything from hardware glitches to software hiccups and daily operation snags:
Fault: Furnace Fails to Heat or Heats Slowly
Possible Causes:
- Blown Fuse: A damaged fuse in the control circuit prevents the heating element from functioning.
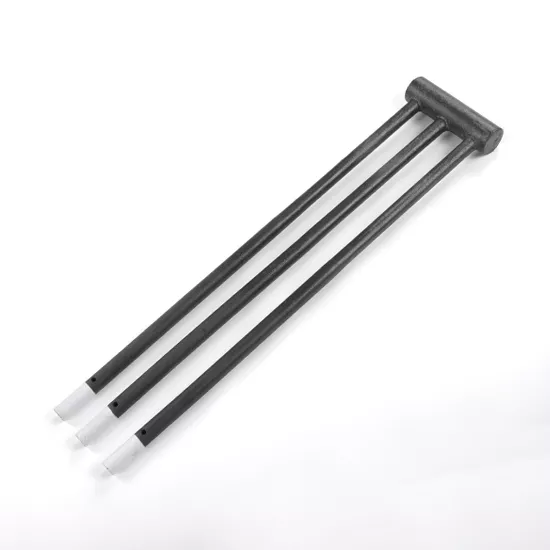
- Aging Heating Elements: Worn MoSi2 heating elements reduce heating efficiency.
- Power Supply Issues: Unstable voltage or loose wiring disrupts operation.
- Temperature Control Failure: Malfunctioning controller or temperature sensor.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the fuse: Access the control cabinet to verify fuse integrity. Replace any damaged fuse with one matching the original specifications.
- Examine heating elements: After powering off, open the furnace cover to check MoSi2 Heating rods for cracks, breaks, or excessive wear. Contact CVSIC for genuine replacement parts if needed.
- Verify power supply: Use a multimeter to confirm input voltage aligns with equipment requirements (typically 220V or 380V) and ensure all wiring connections are secure.
- Assess the temperature control system: Check the controller display for error codes, restart the system, or recalibrate the sensor. For persistent issues, reach out to CVSIC’s technical support team.
CVSIC Heating Element for Dental Furnaces
Fault: Temperature Deviations or Inconsistent Heating
Possible Causes:
- Sensor Drift: Prolonged use reduces temperature sensor accuracy.
- Uneven Heating Elements: Aging MoSi2 rods causes inconsistent furnace chamber temperatures.
- Contaminated Furnace Chamber: Zirconia dust or debris impairs heat transfer.
- Incorrect Sintering Curve: Rapid heating/cooling rates are unsuitable for the material.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Calibrate the sensor: Use specialized calibration tools or contact CVSIC’s technical team for recalibration every 6–12 months.
- Inspect heating elements: Ensure all MoSi2 rods function uniformly; replace any aging components promptly.
- Clean the furnace chamber: Remove dust and residues with a soft brush to prevent contamination of restorations.
- Optimize the sintering curve: To ensure precise zirconia sintering troubleshooting, follow material manufacturer guidelines (e.g., 3M, VITA) to set appropriate heating/cooling rates, typically 2–5°C/min. For a complete understanding, refer to our Sintering Curve and Temperature Control Guidelines, where detailed dental furnace maintenance tips are also available.
Fault: Cracked Restorations or Poor Sintering Quality
Possible Causes:
- Improper Sintering Curve: Rapid heating or cooling induces thermal stress.
- Material Contamination: Furnace chamber residues contaminate zirconia.
- Inferior Sintering Trays or Beads: Low-quality trays cause uneven heating.
- Material Incompatibility: Zirconia properties mismatch the sintering curve.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Review the sintering curve: Ensure heating/cooling rates align with material specifications (2–3°C/min for conventional sintering, 5–8°C/min for fast sintering). See our Fast vs. Conventional Sintering Comparison.
- Maintain a clean furnace chamber: Use CVSIC-recommended high-quality sintering trays and zirconia support beads, cleaning the chamber before each cycle.
- Confirm material compatibility: Verify the zirconia brand’s (e.g., VITA, Ivoclar) recommended sintering parameters and adjust furnace settings accordingly.
Fault: Equipment Errors or Unresponsive Control Panel
Possible Causes:
- Software Issue: Firmware glitches or programming errors.
- Power Instability: Unstable supply or faulty internal wiring.
- Touchscreen Malfunction: Hardware damage or poor connectivity.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Restart the system: Power off the furnace, wait 5 minutes, and restart to check functionality.
- Update firmware: Visit the official website to download the latest firmware and apply updates via OTA.
- Check power stability: Ensure a consistent power supply and inspect control cabinet wiring for loose connections.
- Contact support: If issues persist, reach out to CVSIC’s technical team for remote diagnostics or on-site assistance.
Fault: Overheating or Inadequate Heat Dissipation
Possible Causes:
- Poor Ventilation: Insufficient clearance around the furnace or blocked cooling fans.
- Cooling System Failure: Malfunctioning fans or damaged heat sinks.
- Prolonged Operation: Continuous high-temperature runs cause overheating.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure proper ventilation: Maintain at least 30 cm of clearance around the furnace and clean dust from fans and vents.
- Inspect the cooling system: Verify that cooling fans operate correctly; replace any faulty components.
- Schedule operations: Avoid continuous high-temperature operation for 24 hours; allow the furnace to rest every 8–10 hours.
Practical Maintenance Tips to Prevent Issues
To maximize the lifespan of your dental sintering furnace and minimize downtime, follow these maintenance practices:
- Routine Cleaning: Clean the furnace chamber before each use to prevent dust contamination of restorations.
- Heating Element Checks: Inspect MoSi2 rods every 6 months and replace them every 12–18 months.
- Sensor Calibration: Recalibrate temperature sensors every 6–12 months for precise control.
- Ventilation Maintenance: Ensure adequate airflow around the furnace and clean fans and vents regularly.
- Firmware Updates: Check the manufacturer’s website quarterly for firmware updates to enhance performance.
- Usage Logs: Record sintering parameters and any anomalies to streamline troubleshooting.
Explore more maintenance strategies in our Guide to Extending Dental Furnace Lifespan.
Common Troubleshooting Misconceptions and Solutions
Misconception 1: Neglecting Furnace Chamber Cleaning
- Issue: Dust or residues can contaminate restorations or corrode the chamber.
- Solution: Clean the furnace chamber before each use and employ high-quality sintering trays and support beads.
Misconception 2: Delaying Heating Element Replacement
- Issue: Aging MoSi2 rods causes uneven heating, compromising sintering quality.
- Solution: Inspect rods regularly and replace them as scheduled.
Misconception 3: Relying on Generic Sintering Curves
- Issue: Unsuitable curves may lead to cracked restorations or suboptimal results.
- Solution: Use material-specific parameters from manufacturers. Refer to our Sintering Curve and Temperature Control Guidelines.
Misconception 4: Bypassing After-Sales Support
- Issue: Unauthorized repairs may exacerbate damage.
- Solution: Contact CVSIC’s technical support for complex issues.
Conclusion
Operating at high temperatures for extended periods, dental sintering furnaces are prone to occasional issues. Prompt troubleshooting and regular maintenance ensure consistent performance, preventing costly downtime. CVSIC’s reliable sintering furnaces, backed by dedicated support, empower you to produce high-quality restorations. Learn more by visiting our Dental Furnace or contacting our technical team today!