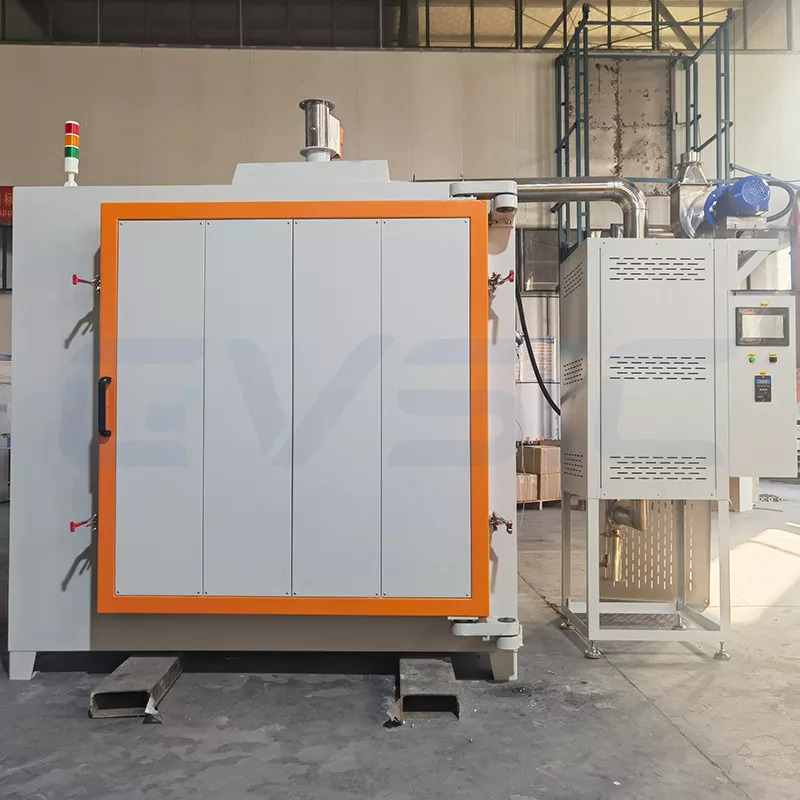
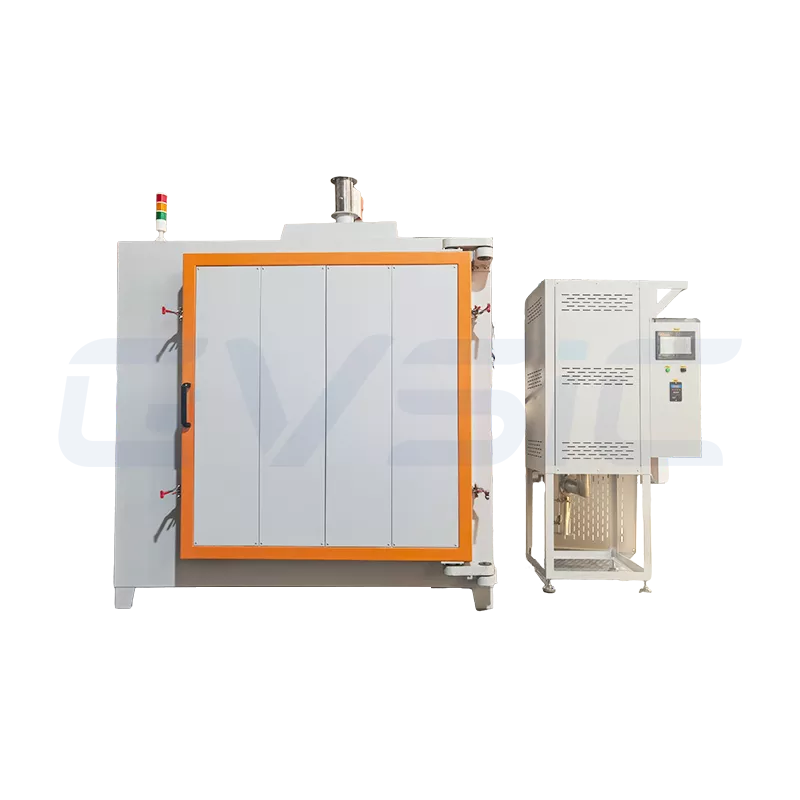
Introduction: Small-Scale or Large-Scale Debinding Furnace?
When it comes to debinding processes, many customers face a dilemma: should they opt for a laboratory-scale debinding furnace for research and experimentation or invest in an industrial-scale debinding furnace for production?
The answer is straightforward:
- Small-scale debinding furnaces are ideal for R&D, experimental production, or low-volume product applications. They offer flexibility and adjustability, perfect for testing new materials and processes.
- Large-scale debinding furnaces are designed for high-volume production, handling large quantities with enhanced automation and stability.
In this guide, CVSIC will compare these two furnace types in detail to help you choose the best fit for your needs.

Design and Purpose of Small-Scale vs. Large-Scale Debinding Furnaces
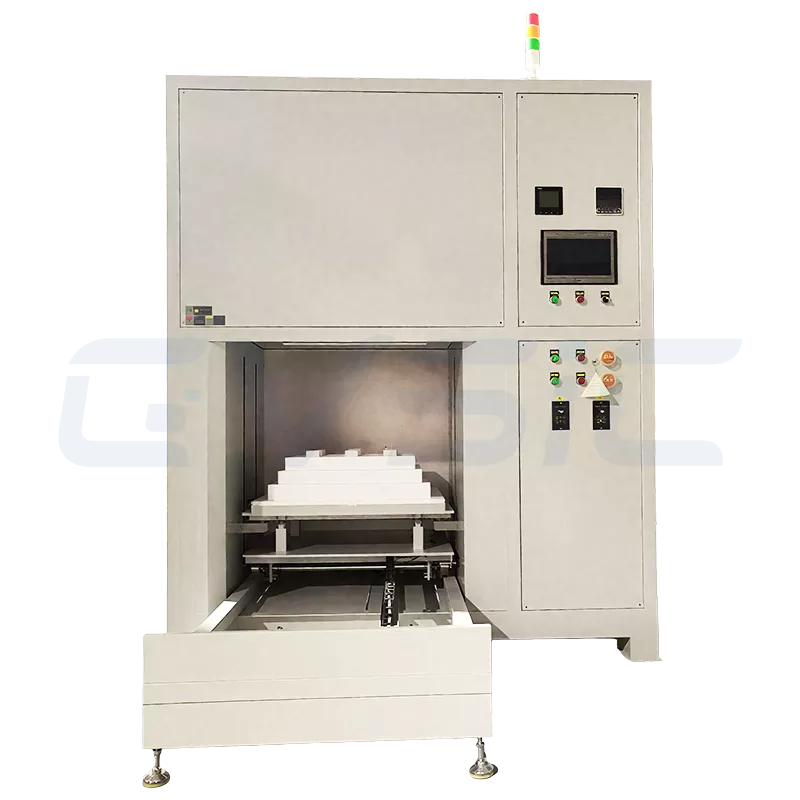
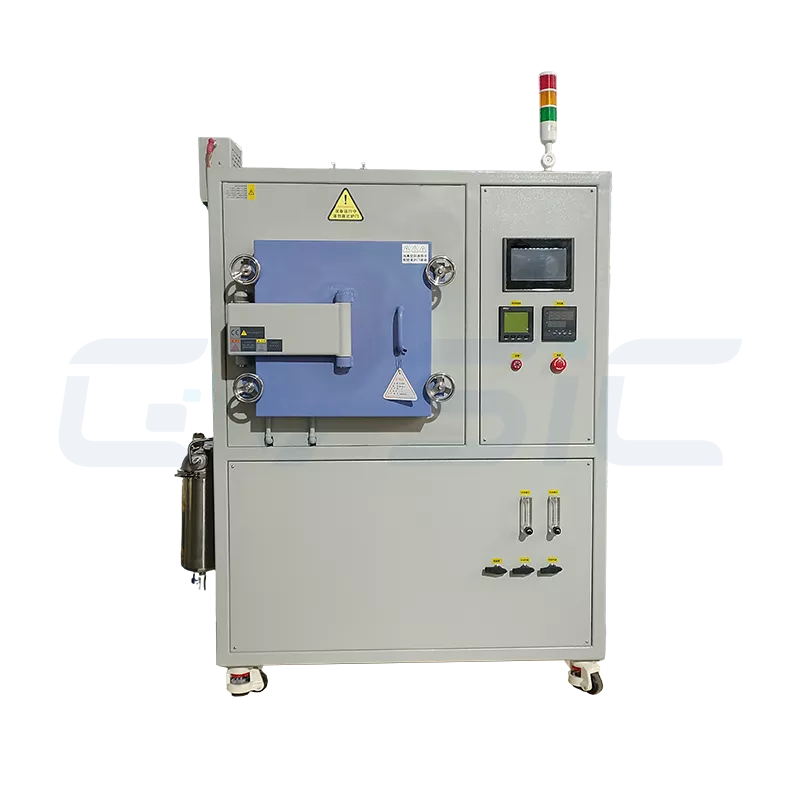
Laboratory Small-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Designed for research, testing, or small-batch production, prioritizing flexibility and precision.
- Compact size (furnace chamber 1–50L), user-friendly operation, and supports multiple debinding methods (e.g., solvent or thermal debinding).
- Common Applications: Developing new materials, debugging MIM (metal injection molding) or CIM (ceramic injection molding) processes, and trial production.
- Key Advantage: Highly flexible, allowing rapid adjustments to temperature, atmosphere, and heating rates.
- Best suited for customers with frequent R&D needs, enabling quick process validation and reduced trial-and-error costs.
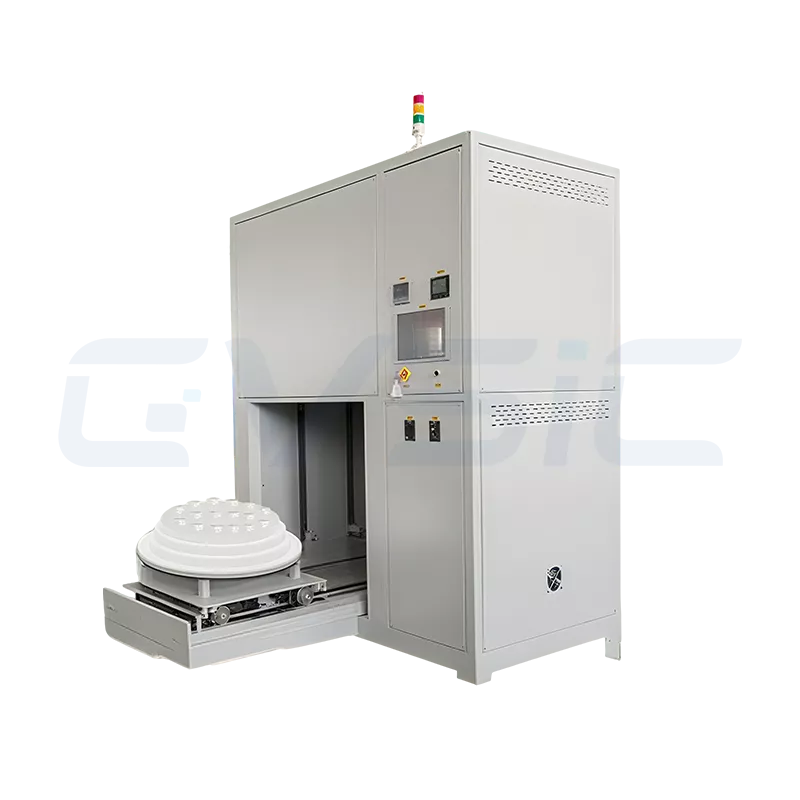
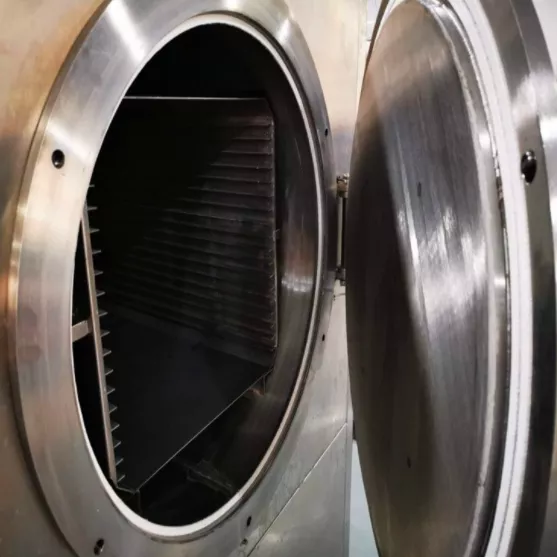
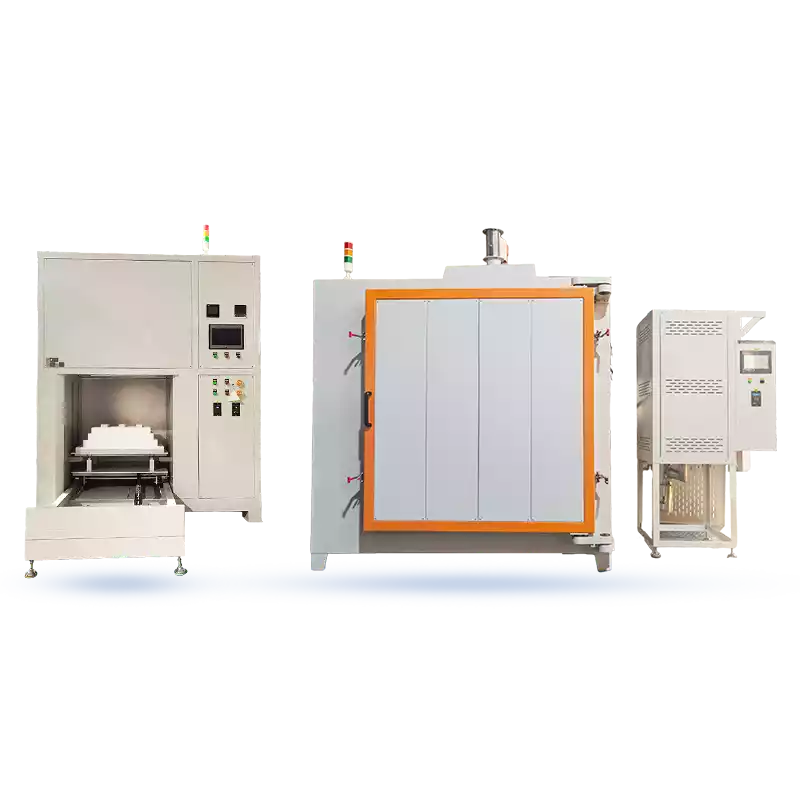
Industrial Large-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Engineered for large-scale, continuous production, emphasizing high throughput and reliability.
- Large furnace chambers (100L–1000L+), often featuring continuous or automated designs for 24/7 operation.
- Common Applications: High-volume MIM production for automotive parts, consumer electronics, and medical devices.
- Key Advantage: Exceptional production efficiency with high automation, ideal for debinding large quantities of parts.
- Perfect for large-scale production with stringent repeatability requirements.
Key Insight: For mass production, large-scale furnaces are the go-to choice; for R&D or trial production, small-scale furnaces offer unmatched flexibility.
Can a Small-Scale Furnace Handle Small-Scale Production?
Yes, but efficiency is limited. For daily outputs exceeding 10 kg, a large-scale furnace is recommended. CVSIC offers transitional models that effectively bridge both needs.
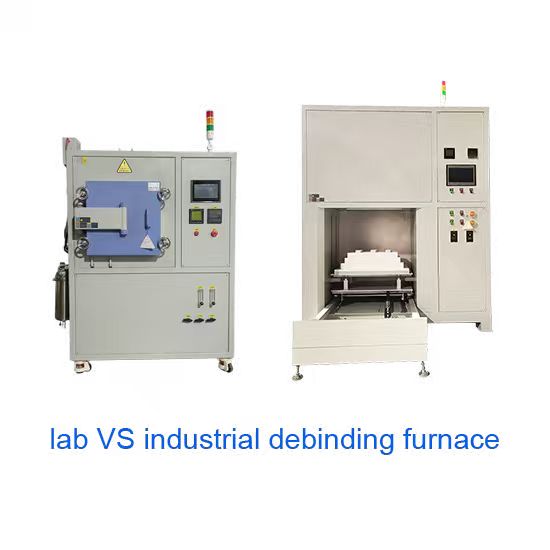
lab vs industrial debinding furnace Structure and Functionality Comparison
| Furnace Chamber Capacity | Small (tens to hundreds of liters) | Large (hundreds to thousands of liters) |
| Atmosphere Control | Simple and adjustable (nitrogen, air, hydrogen, etc.) | Precise and automated (multiple gas pipeline systems) |
| Heating Rate | Fast and customizable | Slower to ensure uniform temperature |
| Automation Level | Low, often manual | High, with automated heating, atmosphere, and exhaust control |
| Applications | R&D, sample testing, process optimization | High-efficiency mass production |
| Equipment Cost | Affordable, ideal for budget-conscious labs | Higher, suited for large-scale enterprises |
Obtain custom degreasing furnaces from CVSIC
Application Scenarios: Which Suits Your Needs?
Laboratory Small-Scale Debinding Furnace
Typical Applications:
- R&D for optimizing MIM or CIM formulations.
- Small-batch production of high-precision parts, such as jewelry or medical devices.
- Educational use in universities or research institutions.
Advantages: Compact, easy to operate, and perfect for rapid experimentation.
Industrial Large-Scale Debinding Furnace
Typical Applications:
- High-volume MIM/CIM for automotive parts or 3C product shells.
- Powder metallurgy for high-strength components like gears and bearings.
- Continuous production with 24/7 operation.
Advantages: High throughput and automation, tailored for industrial production lines.
I produce small-batch MIM parts but occasionally need to scale up. Which should I choose?
A medium-scale debinding furnace (50–100L) strikes a balance between experimentation and small-scale production, with the flexibility to upgrade later.
Cost and Maintenance: Investment vs. Returns
Laboratory Small-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Initial Cost: Affordable (tens to hundreds of thousands of RMB), ideal for labs or startups with limited budgets.
- Operating Cost: Low electricity use and simple maintenance, though manual operation may increase labor time.
- Maintenance Focus: Regular furnace chamber cleaning and monthly thermocouple checks are recommended. CVSIC’s small-scale furnaces include built-in maintenance reminders for user convenience.
- Return on Investment: Perfect for R&D, enabling rapid process validation and faster time-to-market.
Industrial Large-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Initial Cost: Higher (hundreds of thousands to millions of RMB), requiring significant upfront investment.
- Operating Cost: Higher electricity and gas consumption, but lower per-unit costs for large volumes.
- Maintenance Focus: Regular checks on vacuum pumps (for vacuum debinding) or gas pipelines, with quarterly deep maintenance. CVSIC’s remote diagnostics can reduce maintenance costs by up to 50%.
- Return on Investment: Ideal for high-volume production, delivering substantial long-term cost savings.
Key Insight: Small-scale furnaces offer lower costs but may reach capacity limits in production; large-scale furnaces require a higher initial investment but excel in cost efficiency for mass production.
Production Efficiency and Flexibility Comparison
Laboratory Small-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Efficiency: Lower due to smaller batch sizes.
- Flexibility: Highly adaptable, allowing quick parameter adjustments for diverse parts and materials.
Industrial Large-Scale Debinding Furnace
- Efficiency: Exceptional, capable of processing large batches efficiently.
- Flexibility: Less flexible, as parameter changes take longer once set for high-volume production.
Key Insight: Small-scale furnaces are ideal for frequent process tweaks, while large-scale furnaces shine in stable, high-output production.
How to Choose the Right Debinding Furnace?
- Choose a Laboratory Small-Scale Debinding Furnace: If you’re focused on developing new materials, testing processes, or producing high-precision small batches (e.g., laboratory MIM debinding furnace). These are cost-effective and flexible for constrained budgets or spaces.
- Choose an Industrial Large-Scale Debinding Furnace: If you require high-volume production (e.g., for automotive or 3C industries) with a focus on efficiency and low per-unit costs. Ideal for factories with consistent, high-volume orders.
- CVSIC Tip: Beyond equipment cost, consider future capacity growth. Many clients begin with small-scale furnaces for trial production, but upgrade to larger models as their orders increase. Prioritizing scalability in your choice can future-proof your investment.
Conclusion
Selecting between a laboratory-scale debinding furnace and an industrial-scale debinding furnace hinges on your production needs, budget, and growth plans.
Whether you’re in the R&D phase or scaling up for mass production, CVSIC offers customized solutions to streamline your debinding process with efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your needs.