Introduction: Fast Sintering or Conventional Sintering? Select the Right Process for Your Practice
Understanding the differences between fast and conventional sintering enables dental labs to strike a balance between quality and productivity. This comparison from CVSIC summarizes the benefits, limitations, and best uses of each method, guiding your zirconia restoration decisions.
Fast Sintering vs. Conventional Sintering: Key Differences
Fast sintering and conventional sintering are two primary methods for processing zirconia in dental sintering furnaces, distinguished by their sintering duration, temperature ranges, and process designs. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Fast Sintering
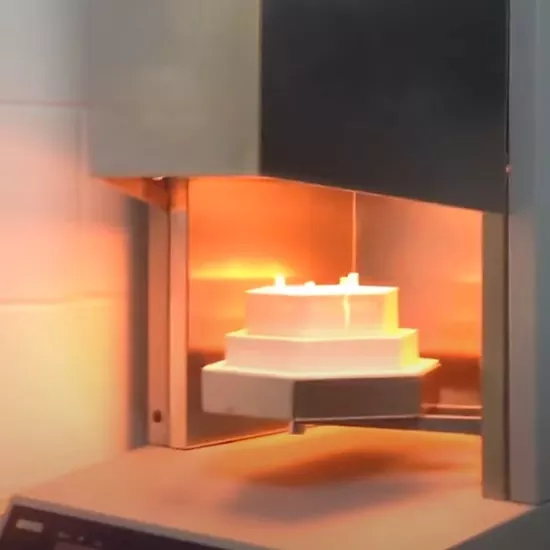
Definition: Uses higher heating rates and shorter periods at target temperature to complete the sintering cycle quickly, typically in 3-4 hours.
Temperature Range: 1500°C–1600°C.
Typical Applications: High-translucency zirconia (a type of ceramic with natural tooth-like transparency), small restorations, and time-sensitive cases.
Process Characteristics:
- Heating rate: 5–8°C per minute.
- Holding time: 1–2 hours.
- Cooling rate: 5°C/min, a moderately rapid rate.
Conventional Sintering
Definition: Uses slower rates for heating and cooling, plus longer holding times at temperature, for a more gradual process, usually taking 6-8 hours.
Temperature Range: 1450°C–1550°C.
Typical Applications: High-strength zirconia (a ceramic formulation favored for its durability), large restorations, and batch production.
Process Characteristics:
- Heating rate: 2–3°C per minute.
- Holding time: 2–3 hours.
- Cooling rate: 2–3°C/min, gradual cooling.
CVSIC zirconia furnaces support both sintering modes, featuring over 100 customizable curves for diverse laboratory needs.

Benefits and Drawbacks of Fast Sintering
Benefits
- Time Efficiency: Saves time, expediting delivery for urgent cases.
- Enhanced Productivity: Allows multiple cycles per day, maximizing productivity.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption with shorter process cycles.
- Advanced Automation: Modern furnaces offer easy operation with automation.
Drawbacks
- Material Constraints: Only specific zirconias labeled as “fast sintering compatible” are suitable.
- Structural Limitations: Not ideal for large bridges or thick-walled restorations, which may experience uneven sintering or cracking.
- Aesthetic Considerations: In some cases, color and translucency may be less refined compared to conventional sintering.
- Thermal Stress Risks: Rapid cooling can introduce microcracks or residual stresses in the material.
CVSIC Recommendation: Our optimized fast sintering mode, combined with high-precision PID (proportional-integral-derivative) temperature control, ensures both efficiency and exceptional restoration quality.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Conventional Sintering
Benefits
- Superior Uniformity:Ensures uniform grain growth for stable structures.
- Broad Compatibility: Supports all zirconia types and brands.
- Consistent Aesthetics: Ideal for multilayer zirconia, preserving natural color.
- Reduced Thermal Stress: Gradual cooling minimizes the risk of cracks due to differential shrinkage.
Drawbacks
- Time-Intensive: Longer cycles are less suited for urgent orders or immediate restorations.
- Higher Energy Use: Extended operation increases energy costs.
- Equipment Downtime: Prolonged cycles may limit furnace availability during peak production.
CVSIC Advantage: Our furnaces utilize advanced insulation to reduce energy consumption in conventional sintering by up to 20%.
Choosing Between Fast Sintering and Conventional Sintering
| Sintering Time | 6–8 hours | 1.5–3 hours |
| Material Compatibility | Broadly applicable | Requires specific materials |
| Applicable Structures | All sizes, including bridges | Single crowns, simple structures |
| Aesthetic Performance | Natural, seamless transitions | Slightly less refined, process optimization needed |
| Equipment Requirements | Standard sintering furnaces | Requires fast sintering curve support |
| Efficiency & Cost | Ideal for planned production | Suited for rapid-response needs |
Purchase high-performance dental furnaces from China Dental Furnace Company
Applications of Fast Sintering and Conventional Sintering
Fast Sintering Applications
- Small Clinics or Urgent Orders: Perfect for processing 5–15 restorations daily with fast turnaround.
- High-Translucency Zirconia: Optimized for high- or ultra-translucent zirconia, ideal for anterior aesthetic restorations.
- High-Throughput Labs: Enables shorter production cycles in modern, high-volume laboratories.
- Examples: Single anterior crowns, small 3-unit bridges, urgent restoration orders.
Conventional Sintering Applications
- Large Labs or Batch Production: Suited for processing over 50 restorations daily with consistent quality.
- High-Strength Restorations: Ideal for long-span bridges or implant abutments requiring superior durability.
- Versatile Zirconia Compatibility: Supports high-strength, high-translucency, and ultra-translucent zirconia brands.
- Examples: Multi-unit bridges, full-mouth restorations, batch crown production.
How to Choose the Right Sintering Method
Selecting between fast and conventional sintering depends on your laboratory’s specific needs. Consider these practical tips:
Evaluate Output and Time Requirements
- Opt for fast sintering for urgent orders or small-batch restorations.
- Choose conventional sintering for high-volume production or restorations requiring maximum strength.
Verify Material Compatibility
- Check sintering parameters from zirconia brands (e.g., 3M, VITA) and select furnaces that support recommended curves.
Assess Equipment Capabilities
- Fast sintering demands precise temperature control (±1°C) and uniform heating; prioritize trusted brands.
- Conventional sintering requires reliable, long-term performance; choose durable furnace models.
Balance Operating Costs
- Fast sintering saves time but requires advanced equipment; conventional sintering offers broader compatibility but higher energy use.
Explore more selection tips in our comprehensive guide to zirconia sintering furnaces.
Critical Temperature Control Considerations for Sintering
Precise temperature control is crucial for achieving high-quality outcomes in both fast and conventional sintering. Key considerations include:
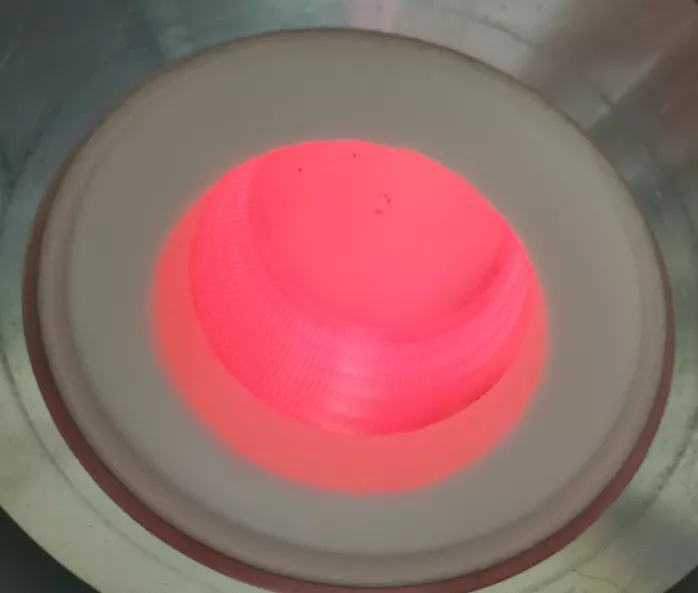
- High-Precision Temperature Control: Fast sintering requires ±1°C accuracy to prevent microcracks from rapid heating.
- Uniform Heating: Multi-point MoSi2 Heating Rods arrangements (specialized heating elements designed for even temperature distribution) ensure steady furnace chamber temperatures. Use high-quality sintering trays (platforms for supporting restorations) and ceramic support beads (small spheres that promote heat flow) to prevent uneven heating.
- Optimized Curve Settings: Fast sintering: 5–8°C/min heating rate, 1–2 hours holding time. (A sintering curve is a preset sequence of temperature changes for the process.)
- Conventional sintering: 2–3°C/min heating rate, 2–3 hours holding time.
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate temperature sensors every 6 months to maintain accuracy.
Practical Tips for Using and Maintaining Sintering Furnaces
Proper operation and maintenance ensure peak furnace performance in both sintering modes:
Usage Tips:
- Keep the furnace chamber clean to prevent zirconia dust contamination.
- Follow manufacturer-recommended sintering curves, especially for fast sintering.
- Use dedicated sintering trays and support beads for uniform heat distribution.
Maintenance Tips:
- Inspect silicon molybdenum rods regularly, replacing them every 12–18 months.
- Remove furnace chamber residues to avoid affecting subsequent cycles.
- Calibrate temperature sensors periodically for consistent accuracy.
Discover more maintenance best practices in CVSIC dental furnace maintenance guide.
Conclusion
Fast and conventional sintering each offers unique benefits, with the best choice depending on your needs. CVSIC furnaces provide versatile, high-performance solutions for a wide range of demands. Learn more by visiting our Dental Furnace or contacting our team.
FAQ
Does rapid sintering compromise the quality of zirconia restorations?
With precise temperature control and optimized curves, fast sintering delivers both efficiency and quality. CVSIC’s fast sintering mode is rigorously tested, achieving a 99% success rate.
What are the benefits of conventional sintering?
Conventional sintering supports a wide range of zirconia materials, offering superior strength and translucency with consistent results, ideal for high-volume production.
How do I choose between fast and conventional sintering?
Select fast sintering for small clinics or urgent orders; opt for conventional sintering for large labs or restorations requiring maximum strength.