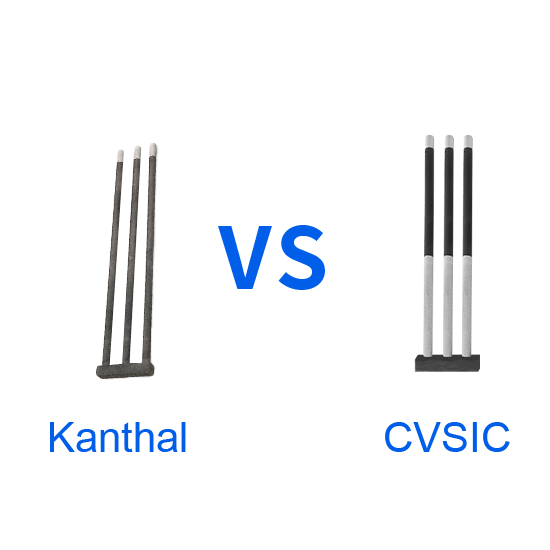
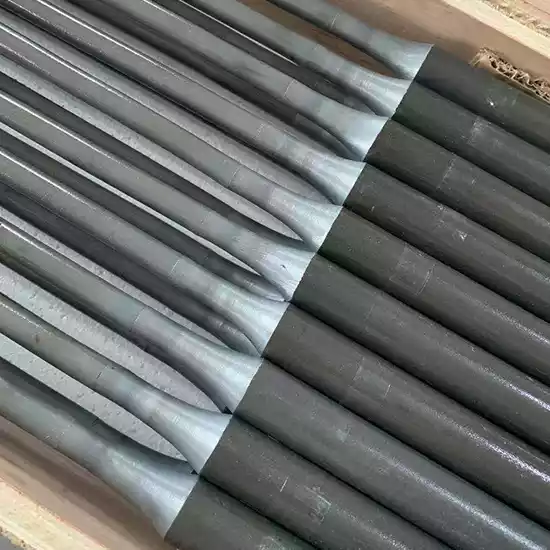
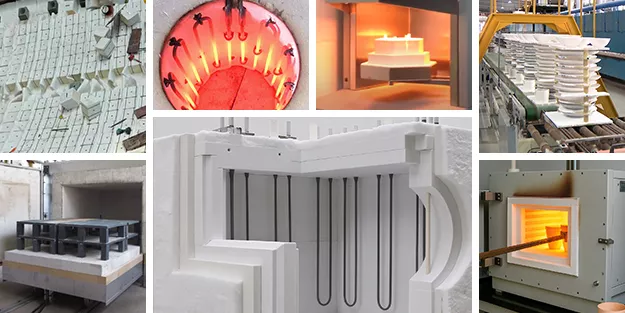
In high-temperature industrial settings, such as ceramic firing, metal heat treatment, or semiconductor production, Silicon Carbide Heating Elements are essential components due to their high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity.
With various shapes, specifications, and brands available, how do you pick the model best suited to your needs? CVSIC provides a practical buyer’s guide that outlines key considerations for selecting SiC heating elements for high-temperature industrial requirements.
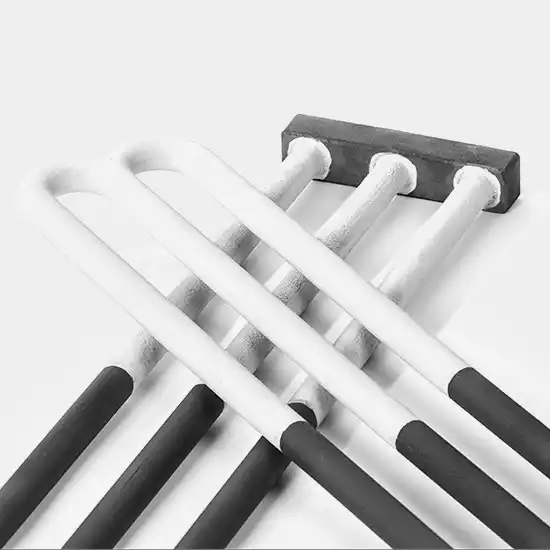

Understanding Silicon Carbide Heating Elements
SiC heating Rods are non-metallic heating components made from high-purity silicon carbide (SiC) material, sintered at temperatures up to 2200°C. Their core advantages include:
- High-Temperature Resistance: Stable operation above 1600°C.
- High thermal conductivity enables fast heat transfer for enhanced energy efficiency.
- Corrosion and Wear Resistance: Ideal for use in acidic and alkaline environments, as well as for long-term applications.
- Diverse Designs: Available in shapes like DB Type, U-shaped, W-shaped, etc., to fit various furnace types.
Different shapes of SiC heating elements have unique reasons for development, features, and applications. Choosing the right one optimizes your production process, extends equipment lifespan, and reduces energy consumption. Below are the key steps for the selection process.
Five Key Factors for Choosing Silicon Carbide Heating Elements
Identify Your Application and Process Needs
Question: What is your heating element used for? Ceramic firing, semiconductor crystal growth, or new energy battery production?
Selection Tips:
- Ceramics and Glass Industry: For ceramic factories, such as those in Jingdezhen, opt for DB Type or U-shaped elements for even heat distribution, ideal for tunnel or roller kilns.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Requires high purity and precise temperature control; prioritize Double-Threaded Type or CVSIC High-Purity SiC Elements for stable wafer processing.
- New Energy Sector: For EV battery sintering, W-shaped or H-shaped elements offer large-area heating and high power output.
Recommendation: Specify your furnace type (box, tunnel, or vacuum) and operating temperature (1000°C–1600°C) to match element performance better.
Select the Right Shape and Size
What is the structure of your furnace, and what is the available furnace space like? Do you need a custom shape?
Standard Shapes and Uses:
- DB Type (Dumbbell Type): Features thicker ends for uniform high-temperature heating, commonly used in ceramics and metal heat treatment applications.
- ED Type (Equal Diameter Type): A cost-effective and easy-to-install option suited for small to medium-sized furnaces.
- U-shaped: Space-saving, ideal for small kilns or semiconductor equipment.
- H-Shaped/W-Shaped: Covers large areas, perfect for large furnaces or new energy applications.
- Single/Double-Threaded Type: Easy to install, suited for high-power or frequent maintenance scenarios.
- Slot Type: Embedded design, ideal for precision ceramics or electronics.
Recommendation: Measure furnace dimensions and available furnace space to ensure the element’s length, diameter, and shape match. CVSIC offers customized designs tailored to your furnace.
Focus on Material Purity and Quality
Question: Can the element operate reliably in the long term? Do impurities affect performance?
Selection Tips:
- High-purity SiC elements minimize the impact of impurities on heating, which is crucial for the semiconductor and new energy industries.
- Check for smooth, crack-free surfaces; quality SiC elements have a hardness of 9.5 on the Mohs scale for durability.
- CVSIC Advantage: Utilises high-purity SiC with low impurity content, making it ideal for high-precision applications and backed by rigorous quality inspections.
Recommendation: Select suppliers with relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and review their product test reports to ensure quality assurance.
Evaluate Power and Energy Efficiency
Question: Does the element meet your power needs? Can it save energy?
Selection Tips:
- Power Matching: Calculate the required power (typically in kilowatts) based on the furnace volume and the target temperature. Ceramic kilns usually need 10–50 kW of power, whereas semiconductor equipment demands precise power control.
- Energy Efficiency: SiC elements’ high thermal conductivity reduces energy use compared to traditional metal heaters.
- Load Capacity: Verify the element’s resistance and maximum current capacity to ensure compatibility with your power system.
CVSIC Highlight: CVSIC elements enhance thermal efficiency, resulting in an average 15% reduction in energy consumption.
Recommendation: Share furnace power requirements with the supplier to ensure matching specifications.
Consider Durability and Maintenance Costs
Question: How long will the element last? What are replacement and maintenance costs?
Selection Tips:
- Durability: High-quality SiC elements can operate at temperatures exceeding 1500 °C for thousands of hours, minimizing the need for replacements.
- Maintenance Ease: Threaded types (single or double-threaded) allow for quick replacements, making them ideal for high-maintenance scenarios.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although high-purity SiC elements are more expensive up front, they ultimately reduce long-term energy and maintenance expenses.
CVSIC Case Study: A Foshan ceramic factory using CVSIC U-shaped elements cut downtime by 20% and maintenance costs by 10%.
Recommendation: Select elements with strong thermal shock resistance and inquire about the supplier’s after-sales support and warranty policies.
How to Choose a Reliable Supplier
- Quick Response: Opt for experienced suppliers like CVSIC for fast response, custom services, and efficient logistics.
- Technical Support: Does the supplier offer installation guidance or process optimization advice?
- Customer Reviews: Check feedback from other users to gauge product quality and the level of after-sales service.
- CVSIC Advantage: As a Chinese brand, CVSIC offers comprehensive support from design to installation, making it an ideal partner for local ceramics, new energy, and semiconductor businesses.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Focusing solely on price can result in low-cost elements with lower purity and shorter lifespans, ultimately leading to increased long-term costs.
- Ignoring Furnace Compatibility: Using the wrong shapes or sizes can cause uneven heating or installation issues.
- Overlooking After-Sales: Lack of technical support can complicate maintenance.
- Recommendation: Weigh performance, cost, and supplier services to maximize long-term value.
Case Study: How CVSIC Helped a Client Choose
A semiconductor company in Zhejiang faced unstable temperature control in its wafer processing furnace. The CVSIC team:
- Needs Analysis: Recommended Double-Threaded SiC elements to meet high-precision heating demands.
- Custom Design: Tailored elements to fit the stove, resulting in a 10% increase in production yield and reduced energy use.