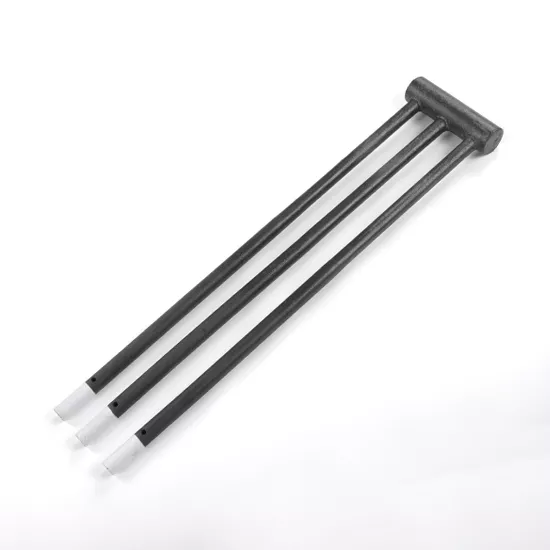
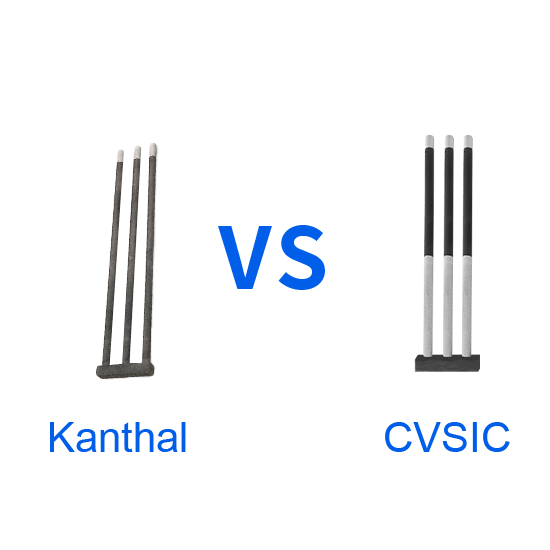
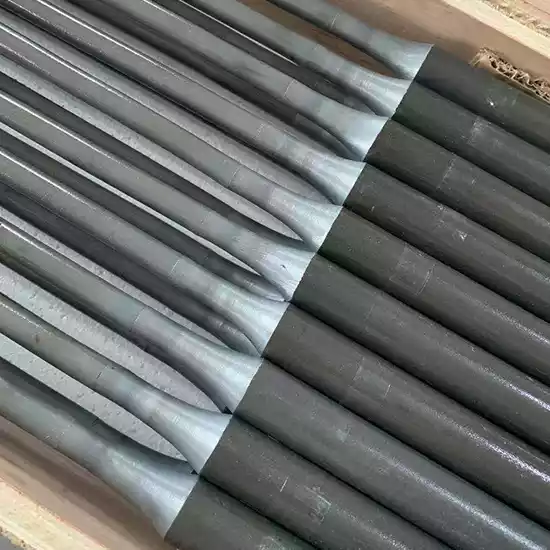
In high-temperature industrial settings, whether it’s ceramic firing, metal heat treatment, or semiconductor crystal growth, Silicon Carbide Heating Elements play an indispensable role.
Renowned for their high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity, these elements come in diverse shapes—such as DB Type, ED Type, U-shaped, H-shaped, W-shaped, Single-Threaded, Double-Threaded, and Slot Type—to meet the varied needs of industrial furnaces and processes.
This article explores the reasons behind these shapes, their unique features, and practical applications, offering industrial users a hands-on guide to selecting the best heating solution.
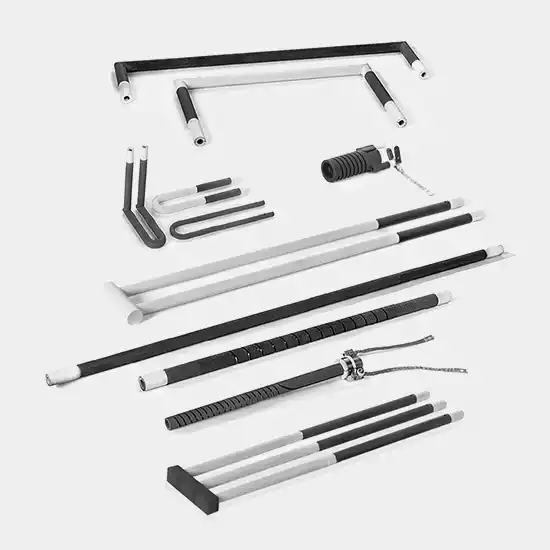

Overview of Silicon Carbide Heating Elements
Silicon carbide heating elements are made from high-purity silicon carbide (SiC) material, sintered at temperatures up to 2200°C, and boast the following core characteristics:
- High-Temperature Resistance: Stable operation above 1600°C.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Fast, uniform heat transfer for energy efficiency.
- Corrosion and Wear Resistance: Ideal for use in acidic and alkaline environments, as well as for long-term applications.
- Flexibility: Multiple shape designs to suit various furnace types.
The variety of shapes arises from the diverse needs of industrial applications, such as furnace structure, heating method (resistive or convective), installation space, and temperature distribution requirements. CVSIC will break down the reasons, features, and applications of each shape.
Analysis of Different Shapes of Silicon Carbide Heating Elements
DB Type (Dumbbell Type)
Reason for Development: The DB Type SiC Heater was designed to meet the need for high-strength support and efficient heating in furnaces. Its “dumbbell” shape, with thicker ends and a slimmer middle, facilitates installation and optimizes heat distribution.

Features:
- Thicker ends enhance mechanical strength, reducing the risk of breakage during installation.
- The slim heating zone concentrates heat for a uniform, high-temperature output.
- Strong thermal shock resistance, ideal for furnaces with frequent on-off cycles.
Applications:
- Ceramic Firing: Used in tunnel kilns, such as those in Jingdezhen’s ceramic factories, for high-temperature porcelain sintering.
- Metal Heat Treatment: Provides uniform high temperatures in annealing furnaces.
- Laboratory Furnaces: Employed in small-scale experimental furnaces for material testing.
ED Type (Equal Diameter Type)
Reason for Development: The ED Type SiC Heater was created to simplify manufacturing and reduce costs. Its uniform diameter supports standardized production while meeting general heating needs.

Features:
- Consistent diameter throughout, simplifying production and lowering costs.
- Even heat distribution is suitable for scenarios with moderate temperature uniformity requirements.
- Flexible installation, suitable for horizontal or vertical placement.
Applications:
- Glass Industry: Used in glass melting furnaces for stable heating.
- Metallurgy: Employed in small to medium-sized furnaces for metal smelting.
- Education and Research: Utilized in university lab heat treatment equipment.
U-Shaped Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The U-shaped SiC element was designed for narrow furnace chambers or scenarios requiring dual-end connections. Its curved shape allows for insertion from the top or side of the furnace, minimizing installation space.

Features:
- A U-shaped structure simplifies connections, with both ends connecting to the power source.
- Heating concentrated at the U-shaped base, ideal for localized high-temperature needs.
- High thermal shock resistance, suitable for rapid heating scenarios.
Applications:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Provides precise high temperatures in crystal growth furnaces.
- Small Kilns: Used in art ceramic studios for firing equipment.
- Chemical Processing: Heats corrosion-resistant chemical reactors.
H-shaped Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The H-shaped SiC element was designed for use in large furnace chambers or multi-zone heating applications. Its crossbeam structure covers a wider heating area, ideal for complex furnace designs.

Features:
- The crossbeam design enhances heating coverage, making it suitable for large workpieces.
- Strong end supports, ideal for suspended installations.
- Broad heat distribution, suited for multi-point heating.
Applications:
- Aerospace: Used in large heat treatment furnaces for aircraft components.
- Industrial Kilns: Provide high temperatures for firing cement or refractory materials.
- New Energy: Employed in photovoltaic cell sintering furnaces.
W-Shaped Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The W-shaped SiC element was designed to enhance heating efficiency and accommodate complex furnace structures. Its multi-fold design increases the heating surface area, which is ideal for high-power demands.

Features:
- The multi-fold structure offers a larger heating area and higher thermal efficiency.
- It suits complex furnace shapes, such as multi-zone kilns.
- It needs precise installation alignment with high mechanical strength.
Applications:
- Ceramic Industry: Used in large roller kilns for high-temperature firing.
- Metallurgical Heat Treatment: Provides uniform heating for significant steel components.
- New Energy Batteries: Employed in lithium battery material sintering furnaces.
Single-Threaded Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The Single-Threaded element was designed for easy installation and replacement. Its threaded end allows for quick connection to electrodes, making it ideal for frequent maintenance scenarios.

Features:
- Single-threaded end enables fast installation and removal.
- Customizable heating zone length, suitable for small to medium furnaces.
- Low contact resistance, maximizing electrical efficiency.
Applications:
- Small Furnaces: Used in jewellery processing or dental ceramic firing furnaces.
- Laboratory Equipment: Provides precise heating for high-temperature experiments.
- Chemical Industry: Delivers stable heat in small-scale reactors.
Double-Threaded Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The Double-Threaded SiC element was designed to enhance connection stability and support high-power applications. Dual-threaded ends improve electrical and mechanical reliability.

Features:
- Dual-threaded ends ensure stable connections, ideal for high-current applications.
- Excellent high-temperature performance, suitable for prolonged operation.
- Higher manufacturing precision, resulting in slightly increased costs.
Applications:
- Semiconductor Production: Provides high-power heating in wafer heat treatment furnaces.
- Industrial Heat Treatment: Used in quenching furnaces for significant metal components.
- New Energy: Employed in fuel cell sintering furnaces.
Slot Type Silicon Carbide Heating Element
Reason for Development: The Slot Type SiC Heater was designed for specialized furnaces or installations that require embedded components. Its slotted structure allows embedding into furnace walls or fixed positions.

Features:
- The slotted design facilitates embedded installation, saving space.
- Heat is concentrated within the slot, making it ideal for localized high-temperature needs.
- Strong resistance to mechanical strain, making it suitable for use in vibrating environments.
Applications:
- Precision Ceramics: Embedded in high-end ceramic firing furnaces.
- Electronics Industry: Used in electronic component heat treatment equipment.
- Research Experiments: Offers customized heating for high-temperature testing setups.
Despite their varied shapes, all silicon carbide heating elements share these advantages:
- High Durability: Hardness up to 9.5 Mohs, far exceeding traditional materials, ensuring long service life.
- Energy Efficiency: High thermal conductivity reduces energy loss, supporting China’s carbon neutrality and peak emissions goals.
- Flexible Customization: Shapes and sizes tailored to furnace and process needs.
- Localized Support: Suppliers like CVSIC offer rapid response and customized services.
Case Study: CVSIC Silicon Carbide Heating Element Application
A ceramic factory in Foshan, Guangdong, struggled with frequent downtime due to failures of traditional heating elements. After adopting CVSIC U-shaped and DB Type Silicon Carbide Heating Elements:
- Results: Downtime is reduced by 25%, thanks to the high durability of SiC elements.
- Data: At 1500°C, CVSIC elements maintained stable performance, resulting in an 18% reduction in energy consumption.
- Customer Feedback: “CVSIC’s U-shaped elements worked perfectly in our kilns, were easy to install, and ramped up our efficiency, making us more competitive.”
Market Trends and Future Outlook
- Demand Drivers: The rapid growth of ceramics, new energy, and semiconductor industries fuels demand for SiC heating elements.
- Technological Innovation: New SiC coatings and customized designs enhance the performance of elements.
- Market Size: The global SiC market is projected to reach USD 9.5 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 17.8%.
- CVSIC’s Contribution: As a Chinese brand, CVSIC is committed to developing efficient and eco-friendly heating elements and supporting industrial upgrades.
Conclusion
The diverse shapes of silicon carbide heating elements—DB Type, ED Type, U-shaped, H-shaped, W-shaped, Single-Threaded, Double-Threaded, and Slot Type—meet the varied needs of applications from ceramic firing to semiconductor manufacturing. CVSIC Silicon Carbide Heating Elements, with their high purity, customised designs, and localised support, provide reliable solutions for Chinese industrial users. Whether you need efficient kiln heating or precision new energy production, CVSIC lights the way forward.
Take Action: Reach out to CVSIC to explore silicon carbide heating solutions tailored to boost your production efficiency.
References
- Kintek Solution
- Global Market Insights
- Innotronix Technology Co., Ltd.